Uterine Fibroids
Introduction:
In India, just like in other parts of the world, many women experience health issues related to their reproductive system. One such common condition is Uterine Fibroids. In this article, we will explore what Uterine Fibroids are, their symptoms, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention techniques. Let's dive in!
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
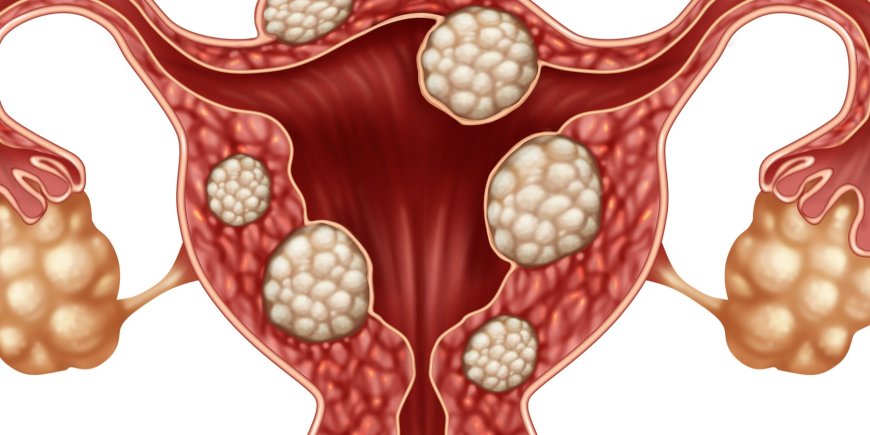
Uterine Fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in the walls of the uterus, which is a part of a woman's reproductive system. These growths are made up of muscle and fibrous tissue and can vary in size, from being as small as a seed to as large as a grapefruit.
Signs and Symptoms:
The symptoms of Uterine Fibroids can vary from woman to woman. Some common signs include:
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: Women may experience prolonged and heavy periods, leading to anemia in some cases.
- Pelvic Pain: Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic region is a common symptom.
- Frequent Urination: Fibroids pressing on the bladder can cause an increased urge to urinate.
- Constipation: Large fibroids can put pressure on the intestines, leading to constipation.
- Enlarged Abdomen: In some cases, fibroids can cause the abdomen to appear swollen or enlarged.
- Infertility or Miscarriages: Depending on their size and location, fibroids may interfere with pregnancy and fertility.
How Are Uterine Fibroids Classified?
Uterine Fibroids can be classified based on their location within the uterus:
- Subserosal Fibroids: These fibroids grow on the outer surface of the uterus and can sometimes create a noticeable bulge.
- Intramural Fibroids: These fibroids develop within the muscular wall of the uterus and can lead to an enlarged uterus.
- Submucosal Fibroids: These fibroids grow just beneath the lining of the uterine cavity and can cause heavy menstrual bleeding and other complications.
Causes and Triggers:
The exact cause of Uterine Fibroids is not fully understood, but several factors can contribute to their development:
- Hormones: Estrogen and progesterone, two hormones involved in the menstrual cycle, seem to play a role in fibroid growth.
- Family History: If a woman's mother or sister has had fibroids, she may be at a higher risk.
- Ethnicity: Studies suggest that women of African descent are more likely to develop fibroids.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of fibroids.
- Age: Fibroids are more common in women aged 30-50.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Let's understand risk factors with examples to explain them better:
- Family History: For example, if Priya's mother had fibroids, Priya may have an increased risk of developing them too.
- Ethnicity: For instance, studies have shown that women of Indian descent may have a higher risk of fibroids.
- Obesity: If Riya is overweight, she might be more prone to developing fibroids compared to her thinner friends.
Types of Uterine Fibroids:
- Subserosal Fibroids: Picture small growths on the outer surface of the uterus, like tiny bumps on a ball.
- Intramural Fibroids: Imagine a small lump growing inside the walls of the uterus, making it bigger.
- Submucosal Fibroids: Picture tiny bumps just under the surface lining of the uterus, like grains under a tablecloth.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
To diagnose Uterine Fibroids, doctors may use several tests:
- Ultrasound: Using sound waves to create images, this test helps doctors see the fibroids and their size.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This advanced imaging test provides detailed pictures of the uterus and fibroids.
- Hysteroscopy: A thin, lighted tube is used to look inside the uterus and identify fibroids.
Treatments for Uterine Fibroids:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to control symptoms like pain and heavy bleeding.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormonal treatments can help shrink fibroids and relieve symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical procedures like Myomectomy or Hysterectomy may be recommended.
Complications of Uterine Fibroids:
- Anemia: Heavy bleeding can lead to low iron levels in the blood.
- Infertility: Depending on the location and size of the fibroids, they may interfere with pregnancy.
- Urinary Problems: Large fibroids can put pressure on the bladder, causing urinary issues.
Prevention Techniques:
While there's no surefire way to prevent fibroids, leading a healthy lifestyle can lower the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Eating a balanced diet and staying active can help prevent obesity, which is a risk factor for fibroids.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can help regulate hormone levels and improve overall health.
- Manage Stress: Stress management techniques like yoga or meditation can be beneficial.
Uterine Fibroids can be a common concern for women, including those in India. Understanding the signs, causes, and risk factors can help women take charge of their health. Regular check-ups and adopting a healthy lifestyle can go a long way in managing fibroids and promoting overall well-being. Remember, knowledge is power, and being informed about our bodies empowers us to make better choices for our health.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0