Uterine Bleeding
Introduction:
Uterine bleeding, also known as abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB), is a medical condition that affects the female reproductive system. It involves excessive or irregular bleeding from the uterus. In India, like in other parts of the world, many women experience uterine bleeding at some point in their lives. Let's explore what uterine bleeding is, its symptoms, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, treatments, and ways to prevent it.
Signs and Symptoms:
Uterine bleeding can cause various signs and symptoms, such as:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding that soaks through pads/tampons quickly.
- Irregular menstrual cycles.
- Bleeding between periods.
- Prolonged periods lasting more than a week.
- Severe menstrual cramps.
- Fatigue due to blood loss.
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy.
What Is Uterine Bleeding? Uterine bleeding refers to abnormal bleeding from the uterus that is different from a normal menstrual cycle. It can occur due to hormonal imbalances, structural issues in the reproductive organs, or other medical conditions.
How Is Uterine Bleeding Classified? Uterine bleeding can be classified into two main types:
- Menorrhagia: Excessive and prolonged bleeding during menstrual periods.
- Metrorrhagia: Irregular bleeding between menstrual periods.
Causes and Triggers: Several factors can lead to uterine bleeding in India, including:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Fluctuations in hormone levels during the menstrual cycle can cause irregular bleeding.
- Uterine Polyps: Small growths in the uterus that can lead to abnormal bleeding.
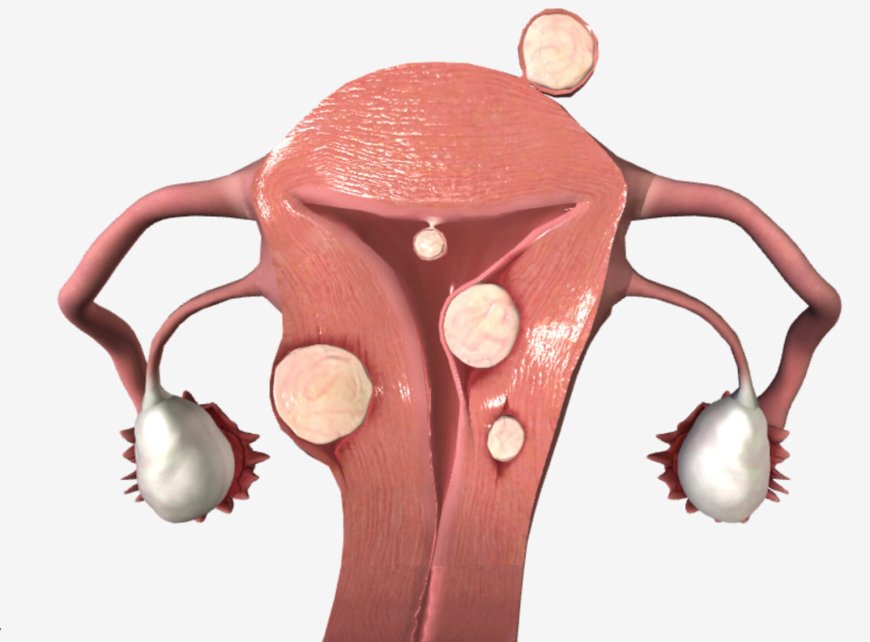
- Fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy periods.
- Endometriosis: When the tissue lining the uterus grows outside of it, it can lead to painful and irregular bleeding.
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome): An endocrine disorder that can cause hormonal imbalances and irregular periods.
- Thyroid Problems: Thyroid disorders can affect menstrual cycles.
- Infections: Infections in the reproductive organs can lead to abnormal bleeding.
Risk Factors with Examples: Certain factors increase the risk of developing uterine bleeding, such as:
- Obesity: Being overweight can disrupt hormone levels and increase the risk of AUB.
- Stress: Emotional stress can influence hormonal balance, leading to irregular periods.
- Family History: If someone in the family has a history of uterine bleeding, the risk may be higher.
- Starting Menstruation Early or Late: Girls who start menstruating very early or very late might experience irregularities.
- Medications: Some medications can affect menstrual cycles.
Types of Uterine Bleeding:
- Menstrual Disorders: These include menorrhagia (heavy periods) and oligomenorrhea (infrequent periods).
- Bleeding During Pregnancy: Occurs as a result of complications like miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
- Postmenopausal Bleeding: Bleeding that occurs after menopause, which may indicate underlying issues.
- Bleeding Disorders: Conditions where the blood doesn't clot properly can lead to excessive bleeding.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
Diagnostic Tests:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the reproductive organs to detect abnormalities.
- Endometrial Biopsy: Involves removing a small piece of the uterine lining for examination.
- Hysteroscopy: A thin, lighted tube is inserted into the uterus to visualize the inside.
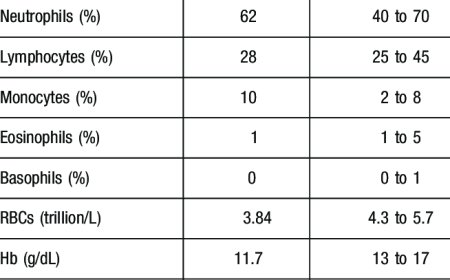
- Blood Tests: Measure hormone levels and rule out other medical conditions.
Treatments:
- Hormonal Therapy: Regulates hormone levels with medications like birth control pills.
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): Scraping the uterine lining to control bleeding.
- Endometrial Ablation: Destroys the uterine lining to reduce bleeding.
- Surgery: In severe cases, procedures like hysterectomy may be considered.
Complications of Uterine Bleeding:
- Anemia: Prolonged heavy bleeding can lead to low iron levels and anemia.
- Infertility: Some underlying causes of uterine bleeding may affect fertility.
- Emotional Distress: Dealing with irregular periods can cause stress and emotional strain.
Prevention Techniques:
While not all uterine bleeding can be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking medical advice for irregularities can help detect and manage the condition early.
Uterine bleeding is a common issue that affects many women in India. Recognizing the signs and symptoms, understanding the causes, and seeking appropriate medical care can help manage the condition effectively. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare professionals are essential for maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0