Urinary Tract Infections
Introduction:
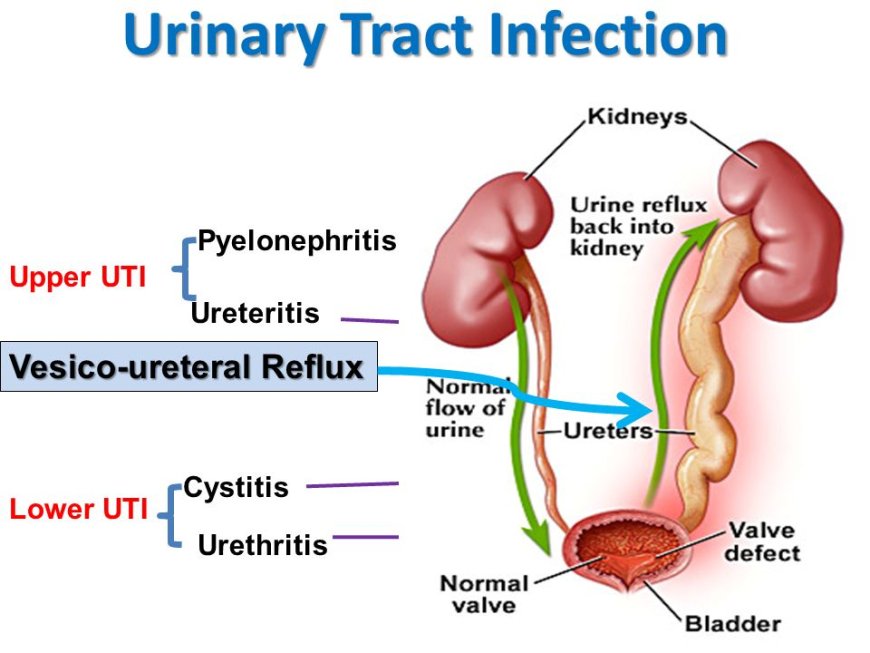
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a common health issue that affects people all around the world, including India. A UTI is an infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters (tubes connecting kidneys to the bladder), bladder, and urethra (tube through which urine exits the body). These infections are caused by harmful bacteria that enter the urinary tract and multiply, leading to various symptoms and discomfort.
Signs and Symptoms:
When someone has a UTI, they may experience the following signs and symptoms:
- Frequent and urgent need to urinate.
- Pain or burning sensation during urination.
- Cloudy or bloody urine.
- Foul-smelling urine.
- Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or back.
- Feeling tired or shaky.
- Fever or chills (in severe cases).
What Is Urinary Tract Infections?
A UTI is like having unwelcome guests (bacteria) in your body's "bathroom" (urinary system). These tiny invaders can cause trouble and make you feel unwell.
How Is Urinary Tract Infections Classified?
UTIs can be classified based on where the infection occurs in the urinary system:
- Bladder Infection (Cystitis): When bacteria infect the bladder, it causes symptoms like frequent urination, pain, and discomfort.
- Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis): If the bacteria move up from the bladder into the kidneys, it can lead to more severe symptoms like back pain, fever, and vomiting.
Causes and Triggers:
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from the digestive tract, like E. coli, which find their way into the urinary system. Some common triggers for UTIs include:
- Poor Hygiene: Not keeping the private parts clean can allow bacteria to grow and cause an infection.
- Holding Urine: When you hold in your pee for too long, it can give bacteria a chance to multiply in the bladder.
- Not Drinking Enough Water: Staying hydrated helps flush out bacteria from the urinary system.
- Voiding Habits: Not emptying the bladder completely during urination can lead to UTIs.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain factors can increase the risk of UTIs, and here are some examples:
- Gender: Girls and women are more prone to UTIs because their urethra is shorter, making it easier for bacteria to enter.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes may have weaker immune systems, making them more susceptible to infections.
- Urinary Catheters: People with long-term catheter use, like those with certain medical conditions, have a higher risk of UTIs.
- Constipation: If you have trouble passing stool regularly, it can increase the risk of UTIs.
Types of Urinary Tract Infections:
There are mainly two types of UTIs based on the part of the urinary system affected:
- Lower UTI: Involving the bladder and urethra, causing symptoms like frequent urination and pain during peeing (cystitis).
- Upper UTI: Affecting the kidneys, leading to symptoms like back pain, fever, and vomiting (pyelonephritis).
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
To diagnose UTIs, doctors may perform the following tests:
- Urinalysis: A urine sample is checked for bacteria, blood cells, and other signs of infection.
- Urine Culture: If bacteria are found in the urine, this test helps identify the specific type and guide appropriate treatment.
Treatments:
- Antibiotics: These are medicines that kill the bacteria causing the infection. Doctors prescribe the right antibiotics based on the urine culture results.
- Increased Fluid Intake: Drinking lots of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary system.
- Pain Relief: Medications can help relieve pain and discomfort during urination.
- Rest and Good Hygiene: Getting enough rest and maintaining proper hygiene aid in the recovery process.
Complications of UTIs:
If left untreated, UTIs can lead to more severe problems, including kidney infections, which may require hospitalization and stronger medications.
Prevention Techniques:
To prevent UTIs, you can follow these simple steps:
- Drink Plenty of Water: Staying hydrated helps keep your urinary system clean.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Keep your private parts clean and wipe from front to back after using the bathroom.
- Use the Bathroom Regularly: Don't hold your pee for too long; visit the bathroom when you need to.
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of harsh soaps or perfumes in the genital area, as they can cause irritation.
if you ever feel any discomfort while urinating or have pain in your belly or back, it's essential to tell a grown-up right away. UTIs can be treated easily when caught early, so don't be afraid to talk about it with your parents or a doctor!
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0