Urethral Cancer
Introduction:
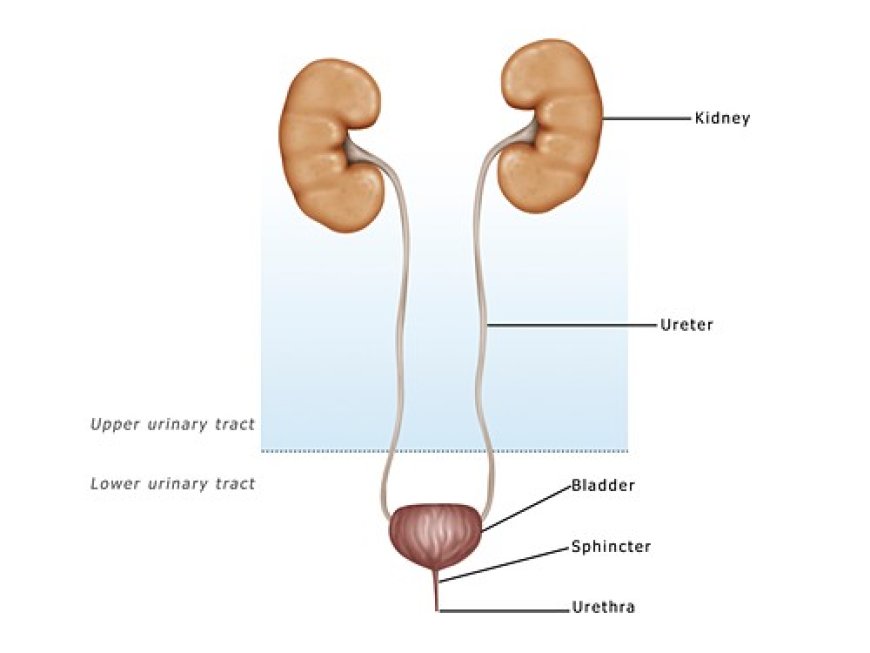
Imagine your body as a big city with roads and buildings, and each road has a special name and purpose. One of the important roads in the city is called the "urethra." It is like a tiny tunnel that helps us pass urine from our body. Sometimes, like in any city, there can be trouble in the form of a disease called "Urethral Cancer." Let's understand this condition in simple language.
What is Urethral Cancer?
Urethral cancer is a rare type of cancer that affects the urethra. The urethra is a tube that connects the bladder (where urine is stored) to the outside of the body. When cells in the urethra start growing abnormally, they form a mass or tumor, and that's when we call it urethral cancer.
Signs and Symptoms:
Just like how a red flag warns us of danger, our body also gives us warning signs when something is not right. If you notice any of these signs, it's important to tell your parents or guardians:
- Difficulty in Peeing: Feeling pain or discomfort while peeing is one of the signs of urethral cancer.
- Blood in Urine: If you see blood in your pee, it might be a signal that something is not okay.
- Changes in Urinary Habits: Suddenly needing to pee more often or feeling an urgent need to pee can be a symptom.
- Lumps or Swelling: If you feel a lump or swelling near the urethra, it's essential to get it checked by a doctor.
How Is Urethral Cancer Classified?
Just like we have different kinds of cars on the road, there are also different types of urethral cancer. They are classified based on where they start in the urethra:
- Anterior Urethral Cancer: This type starts in the front part of the urethra, near the opening where urine comes out.
- Posterior Urethral Cancer: It begins in the back part of the urethra, closer to the bladder.
Causes and Triggers:
Scientists are still trying to understand why urethral cancer happens, but they have found some factors that may increase the risk of developing it:
- Age: Just like some toys are suitable for certain ages, urethral cancer mostly affects older people.
- Smoking: Being around cigarette smoke or smoking can increase the risk.
- Infections: Infections in the urinary tract can sometimes play a role.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections: Some infections passed through intimate contact may also be linked to this cancer.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Risk factors are like some ingredients in your favorite dish that make it a bit more challenging to handle. Here are some examples of risk factors for urethral cancer:
- Example 1: If Grandpa, who is above 60, has been smoking for many years, he might have a higher risk of getting urethral cancer.
- Example 2: If Uncle John had a bad urinary infection that he ignored for a long time, it could increase his chances of developing urethral cancer.
Types of Urethral Cancer with Detailing:
Now, let's take a look at the different types of urethral cancer and where they start:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This type usually begins in the cells that line the urethra and is the most common form.
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma: It starts in the cells of the bladder but can sometimes spread to the urethra.
- Adenocarcinoma: This rare type begins in the glandular cells of the urethra.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
When a doctor suspects urethral cancer, they may use different tools and tests to find out for sure:
- Cystoscopy: The doctor uses a thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera to look inside the urethra and bladder. It helps them see any abnormalities.
- Biopsy: If something suspicious is seen during a cystoscopy, the doctor may take a small sample (biopsy) to examine it under a microscope for cancer cells.
Complications of Urethral Cancer and Prevention Techniques:
If urethral cancer is not caught early, it can cause complications:
- Spread to Other Organs: The cancer cells can travel to other parts of the body, making it harder to treat.
- Blockage: A large tumor can block the urine flow, causing pain and swelling.
To reduce the risk of urethral cancer:
- Stay Away from Smoking: Avoid smoking or being near smoke.
- Hygiene: Practice good hygiene and stay away from harmful infections.
- Regular Checkups: Visit the doctor regularly for checkups.
just like brave superheroes fight villains to protect the city, doctors and medical treatments work hard to fight urethral cancer. So, always listen to your body, and if you ever notice any signs of trouble, don't be afraid to ask for help from grown-ups and doctors who will be there to protect and take care of you.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0