Upper Limb Spasticity (ULS)
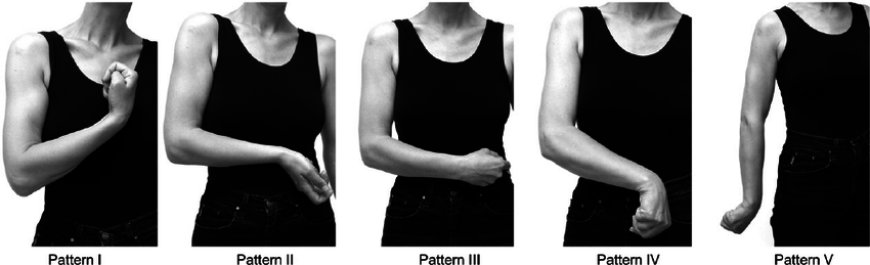
Introduction:
Upper Limb Spasticity (ULS) is a condition that affects the muscles in the arms and hands, making them stiff and difficult to move. It is a common health issue in India, and it is essential to raise awareness about it to promote early diagnosis and effective management. In this article, we will discuss what ULS is, its signs and symptoms, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, and treatment options, all explained in simple language for easy understanding by children.
What Is Upper Limb Spasticity (ULS)? :
ULS is a condition where the muscles in the upper limbs (arms and hands) become stiff and tight due to increased muscle tone. This increased tone is known as spasticity, which can lead to difficulty in performing everyday tasks.
Signs and Symptoms:
The signs and symptoms of ULS can vary, but some common ones include:
- Muscle Stiffness: The muscles in the arms and hands may feel tight and difficult to move.
- Limited Range of Motion: Children with ULS may find it challenging to fully extend or flex their arms and hands.
- Involuntary Muscle Contractions: Spasticity may cause involuntary muscle contractions, leading to jerky movements.
How Is Upper Limb Spasticity (ULS) Classified? :
ULS is classified based on the severity and location of the spasticity. It can be classified as mild, moderate, or severe. The spasticity can affect one or both arms.
Causes and Triggers:
ULS is often caused by damage to the brain or spinal cord, which can occur due to various factors, including:
- Birth Injuries: In some cases, ULS may result from injuries during birth, leading to brain damage.
- Cerebral Palsy: Children with cerebral palsy, a neurological disorder, may develop ULS.
- Stroke: Brain damage from a stroke can also cause ULS in some cases.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing ULS, such as:
- Premature Birth: Children born prematurely may have a higher risk of ULS due to potential brain damage.
- Infections: Infections during pregnancy can increase the risk of ULS in the baby.
Types of Upper Limb Spasticity (ULS) with Detailing:
ULS can be classified into three main types based on the severity of spasticity:
- Mild ULS: In this type, the spasticity is minimal, and the child can perform most activities without significant difficulty.
- Moderate ULS: Children with moderate ULS may face challenges in performing certain activities, and their muscle stiffness may be more noticeable.
- Severe ULS: In severe ULS, the spasticity is significant, and it can severely impact the child's ability to move their arms and hands.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
To diagnose ULS, doctors may perform:
- Physical Examination: Doctors will assess muscle tone and movements in the arms and hands.
- MRI or CT Scan: These imaging tests may be done to identify any brain or spinal cord abnormalities.
Treatment for ULS may include:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy helps improve muscle strength and flexibility.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy focuses on helping children perform daily activities more easily.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to reduce spasticity.
ULS is a condition that can impact a child's ability to move their arms and hands freely. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve a child's quality of life. Parents and caregivers must be aware of the signs and seek medical help if they suspect their child has ULS. With the right support and care, children with ULS can lead happy and fulfilling lives.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0