Unstable Angina
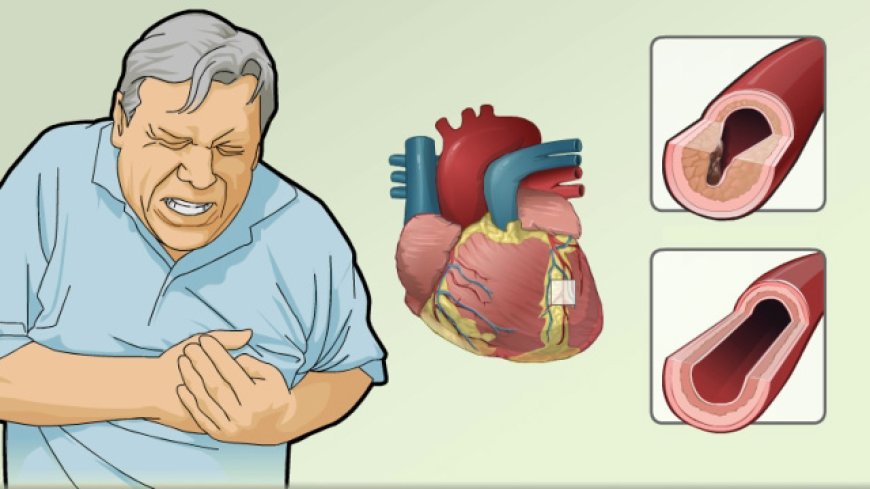
Introduction:
Unstable Angina is a serious medical condition that affects the heart and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. It is a type of chest pain that occurs when the heart muscle doesn't receive enough blood and oxygen. In India, where heart disease is a significant health concern, understanding Unstable Angina is crucial for early detection and proper management. In this article, we will explore what Unstable Angina is, its classification, signs, and symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic tests, treatments, and complications, all explained in simple language for 10-year-old children to comprehend.
What Is Unstable Angina? :
Unstable Angina is a type of chest pain that occurs when there is a partial blockage in the blood vessels that supply the heart with blood. Unlike stable angina, which is predictable and usually triggered by physical activity or stress, unstable angina is unexpected and can happen even at rest. It is a severe condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Chest Pain: The primary symptom of Unstable Angina is severe chest pain or discomfort. The pain may feel like pressure or squeezing in the chest and can radiate to the left arm, jaw, back, or neck.
- Shortness of Breath: Individuals may experience difficulty in breathing, especially during physical activity or when lying down.
- Nausea and Fatigue: Unstable Angina can cause feelings of nausea and extreme tiredness.
How Is Unstable Angina Classified? :
Unstable Angina is classified based on its frequency and severity:
- New-Onset Unstable Angina: This type occurs for the first time and is not related to any specific activity or trigger.
- Crescendo Angina: This type involves increasingly severe and frequent episodes of chest pain.
- Refractory Angina: In this type, the chest pain is persistent and does not respond to usual medications or treatments.
Causes and Triggers:
Unstable Angina is primarily caused by the buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the coronary arteries, which reduces blood flow to the heart muscle. The plaque can rupture, leading to the formation of a blood clot, further obstructing blood flow.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing Unstable Angina in India:
- Smoking: Exposure to secondhand smoke or smoking at a young age can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of Unstable Angina.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, can strain the heart and arteries, contributing to Unstable Angina.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can lead to various heart-related problems, including Unstable Angina.
Types of Unstable Angina:
- New-Onset Unstable Angina: Occurs suddenly and is not related to any prior heart condition.
- Crescendo Angina: Symptoms become more frequent and severe over time.
- Refractory Angina: The chest pain persists and is resistant to conventional treatments.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A painless test that records the heart's electrical activity to detect any irregularities.
- Blood Tests: These help measure certain enzymes that indicate heart muscle damage.
- Coronary Angiography: A procedure that uses a dye to visualize the coronary arteries and identify blockages.
- Medications: Aspirin, nitroglycerin, and other medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms and prevent blood clots.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking can improve heart health.
Complications of Unstable Angina:
If left untreated, Unstable Angina can lead to heart attack or even heart failure.
Unstable Angina is a critical heart condition that requires immediate medical attention. By recognizing the signs and symptoms and understanding the risk factors, individuals can take steps to protect their heart health in India. Regular health check-ups, a heart-healthy lifestyle, and timely medical intervention can significantly reduce the impact of Unstable Angina and promote a healthy heart for life.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0