Umblical hernia in children
Introduction:
Umbilical hernia is a common condition in children, including those in India. It is essential for parents and caregivers to be aware of this condition and seek appropriate medical attention if needed. In this article, we will discuss what umbilical hernia is, its signs and symptoms, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, and treatment options, all explained in simple language for easy understanding by children.
What Is Umbilical Hernia in Children? :
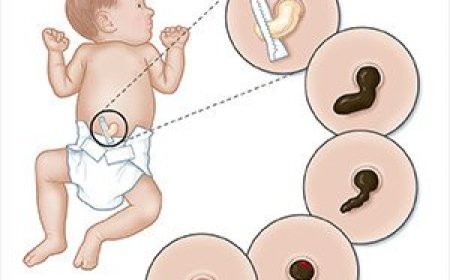
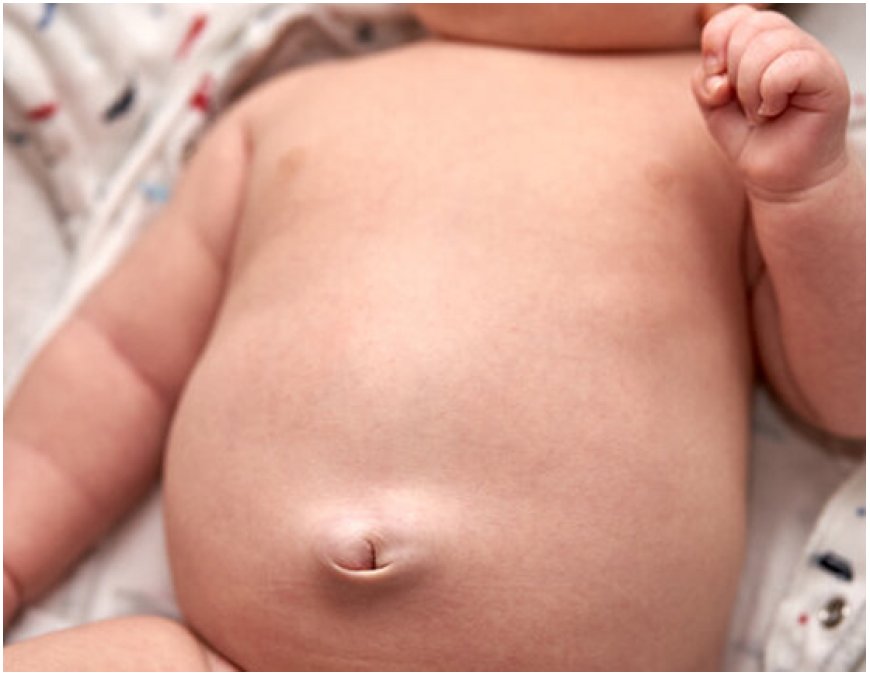
Umbilical hernia is a condition where the child's belly button (umbilicus) bulges out due to a small opening or weak spot in the abdominal muscles. It is often noticeable when the child cries, coughs, or strains.
Signs and Symptoms:
The signs and symptoms of umbilical hernia in children include:
- Belly Button Bulge: The most noticeable sign is the bulge around the belly button area, especially when the child is active.
- Painless: Umbilical hernias are usually painless and do not cause discomfort to the child.
- Reducible: In some cases, the bulge can be easily pushed back into the abdomen when the child is lying down.
How Is Umbilical Hernia in Children Classified? :
Umbilical hernia in children is classified based on the size of the hernia and whether it can be easily reduced (pushed back) or not. It can be classified as reducible or non-reducible.
Causes and Triggers:
Umbilical hernias in children occur due to a weakness in the abdominal muscles around the umbilicus. The exact cause is not always clear, but some factors that may contribute to its development include:
- Birth: Some babies are born with a weak abdominal wall, making them more prone to umbilical hernias.
- Premature Birth: Premature babies may have a higher risk of developing umbilical hernias.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain factors may increase the risk of umbilical hernia in children, such as:
- Family History: Children with a family history of umbilical hernia may have a higher risk of developing one themselves.
Types of Umbilical Hernia in Children with Detailing:
- Reducible Hernia: In this type, the bulge can be easily pushed back into the abdomen, and it is not painful.
- Non-Reducible Hernia: In non-reducible hernias, the bulge cannot be pushed back into the abdomen, and medical attention is required.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments: To diagnose an umbilical hernia, doctors may perform:
- Physical Examination: Doctors will assess the bulge and its characteristics.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, ultrasound or X-ray may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for umbilical hernia in children may include:
- Observation: Many umbilical hernias close on their own as the child grows, so doctors may choose to observe it without any intervention.
- Surgery: If the hernia does not close on its own or if it becomes non-reducible, surgery may be recommended to repair the abdominal wall.
Umbilical hernia is a common condition in children, and most cases do not cause any harm. However, it is essential for parents to be aware of the signs and seek medical advice if needed. With proper care and treatment, children with umbilical hernia can lead healthy and active lives.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0