Thalessamia
Introduction:
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that affects many children in India. It is essential to create awareness about this condition to promote early diagnosis and appropriate management. In this article, we will discuss what Thalassemia is, its signs and symptoms, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, and treatment options, all explained in simple language for easy understanding by children.
What Is Thalassemia? :
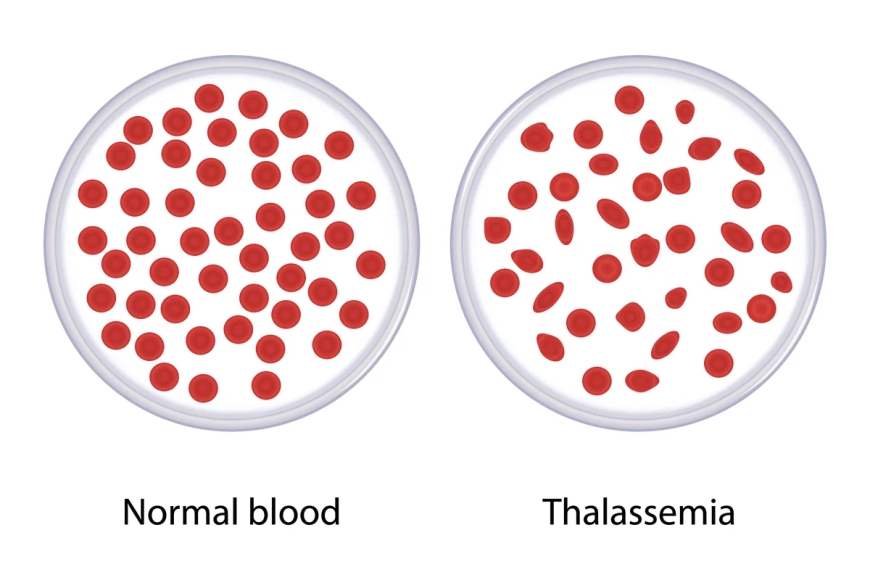
Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. Children with Thalassemia may have anemia, which means their bodies don't have enough healthy red blood cells to function properly.
Signs and Symptoms:
The signs and symptoms of Thalassemia can vary, but some common ones include:
- Fatigue: Children may feel tired and weak due to low oxygen levels in their body.
- Pale Skin: Anemia can cause the skin to appear pale or yellowish.
- Slow Growth: Thalassemia can affect a child's growth and development.
- Enlarged Spleen: The spleen, an organ that filters blood, may become larger in some children with Thalassemia.
How Is Thalassemia Classified? :
Thalassemia is classified based on the type and severity of the condition. The two main types are:
- Alpha Thalassemia: It occurs when there is a problem with the alpha globin protein.
- Beta Thalassemia: This type results from a mutation in the beta globin protein.
Causes and Triggers:
Thalassemia is caused by genetic mutations passed down from parents to their children. If both parents carry Thalassemia genes, their child has a higher risk of inheriting the disorder. It is essential for parents to get tested for Thalassemia before planning a family.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Some children may have a higher risk of Thalassemia due to factors like:
- Family History: If other family members have Thalassemia, the child may be at risk.
- Ethnic Background: Thalassemia is more common in certain ethnic groups, including people of Indian, Mediterranean, or Southeast Asian descent.
Types of Thalassemia with Detailing:
There are four main types of Thalassemia:
- Thalassemia Minor: People with Thalassemia minor have one Thalassemia gene and usually have mild symptoms or no symptoms at all.
- Thalassemia Trait: A person with Thalassemia trait carries one Thalassemia gene from one parent and one normal gene from the other parent.
- Beta Thalassemia Intermedia: Children with this type may have moderate to severe symptoms.
- Beta Thalassemia Major (Cooley's Anemia): This is the most severe form of Thalassemia, and children with this type require regular blood transfusions and medical management.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
To diagnose Thalassemia, doctors may perform:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can measure hemoglobin levels and identify specific types of Thalassemia.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic tests can confirm the presence of Thalassemia genes.
Treatment for Thalassemia may include:
- Blood Transfusions: Children with severe Thalassemia may require regular blood transfusions to maintain healthy hemoglobin levels.
- Iron Chelation Therapy: Due to frequent blood transfusions, excess iron can build up in the body, and chelation therapy helps remove it.
- Folic Acid Supplements: Folic acid supplements are given to support red blood cell production.
Thalassemia is a significant health concern in India, and early detection and management are crucial for better outcomes. Parents must be aware of their family history and get tested for Thalassemia to ensure a healthy future for their children. With appropriate medical care and support, children with Thalassemia can lead fulfilling lives.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0