Quitting Smoking

Introduction:
Smoking is a dangerous habit that affects millions of people around the world, including India. It's a practice where people inhale the smoke from burning tobacco, causing various health problems. Quitting smoking is the process of stopping this habit permanently. In this article, we'll explore what quitting smoking entails, its signs and symptoms, different types, risk factors, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention techniques, all explained in a way that a 10-year-old can easily understand.
Signs and Symptoms of Smoking:
- Persistent Cough: Smokers often have a chronic cough as the smoke irritates their lungs.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty in breathing, especially during physical activities, is common.
- Reduced Taste and Smell: Smoking can dull the sense of taste and smell.
- Yellow Teeth and Fingers: Tar and nicotine can stain teeth and fingers yellow.
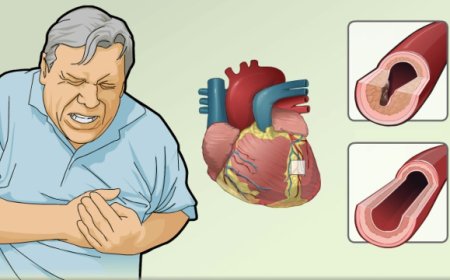
- Increased Heart Rate: Smoking can make the heart beat faster, putting strain on it.
- Dizziness and Headaches: Nicotine can cause these symptoms, especially during smoking or withdrawal.
What Is Quitting Smoking?
Quitting smoking is the process of giving up tobacco and overcoming nicotine addiction. It involves breaking the habit of smoking and adopting a healthier lifestyle.
How Is Quitting Smoking Classified?
- Cold Turkey: Some people quit smoking abruptly, without any assistance or gradual reduction.
- Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): This involves using products like patches, gum, or lozenges to slowly reduce nicotine intake.
- Medications: Certain medications can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms during the quitting process.
- Behavioral Therapies: These therapies help individuals cope with triggers and develop healthier habits to replace smoking.
Causes and Triggers:
Several factors contribute to smoking and make it challenging to quit. Some common causes and triggers include:
- Peer Pressure: If friends or family members smoke, one may feel pressured to try it.
- Stress: People often turn to smoking as a way to cope with stress and anxiety.
- Addiction: Nicotine in tobacco products is highly addictive, making it tough to quit.
- Social Situations: Being around other smokers can trigger the urge to smoke.
Risk Factors with Examples:
-
Health Issues: Smoking increases the risk of lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory problems. Example: Mr. Sharma, a heavy smoker, developed chronic bronchitis due to smoking.
-
Pregnancy Complications: Smoking during pregnancy can harm the baby's growth and cause premature birth. Example: Mrs. Khan's smoking led to low birth weight in her newborn.
-
Secondhand Smoke: Being exposed to other people's smoke can also harm non-smokers. Example: Rahul developed asthma because his parents smoked at home.
Types of Quitting Smoking:
- Unassisted Quitting: Some individuals decide to quit suddenly without any help.
- Assisted Quitting: This includes using products like nicotine patches, gum, or medications.
- Counseling and Support Groups: Joining support groups or seeking counseling for motivation and guidance.
- Combination Approach: Using a combination of methods for better success in quitting.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
-
Diagnostic Tests: Doctors usually assess a person's smoking history and perform lung function tests to determine the impact of smoking on their health.
-
Treatments: a. Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): Helps gradually reduce nicotine dependency. b. Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. c. Behavioral Therapy: Counseling and support groups can provide coping strategies. d. Mobile Apps: Some apps provide motivation and assistance during the quitting process.
Complications of Quitting Smoking:
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Nicotine withdrawal can cause irritability, headaches, and mood swings.
- Weight Gain: Some people gain weight after quitting smoking, but healthy eating and exercise can help manage this.
- Relapse: It's common to experience setbacks while quitting smoking, but persistence is crucial.
Prevention Techniques:
- Education: Teaching children about the dangers of smoking and the benefits of a smoke-free life.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Encouraging physical activities and nutritious diets to maintain good health.
- Supportive Environment: Creating smoke-free homes and public spaces to reduce exposure to smoking.
Quitting smoking is a significant step towards a healthier India. By understanding the signs, symptoms, and various methods of quitting, we can make informed decisions to lead a smoke-free life. With the right support, determination, and preventive measures, we can create a smoke-free future for our country.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0