Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Introduction:
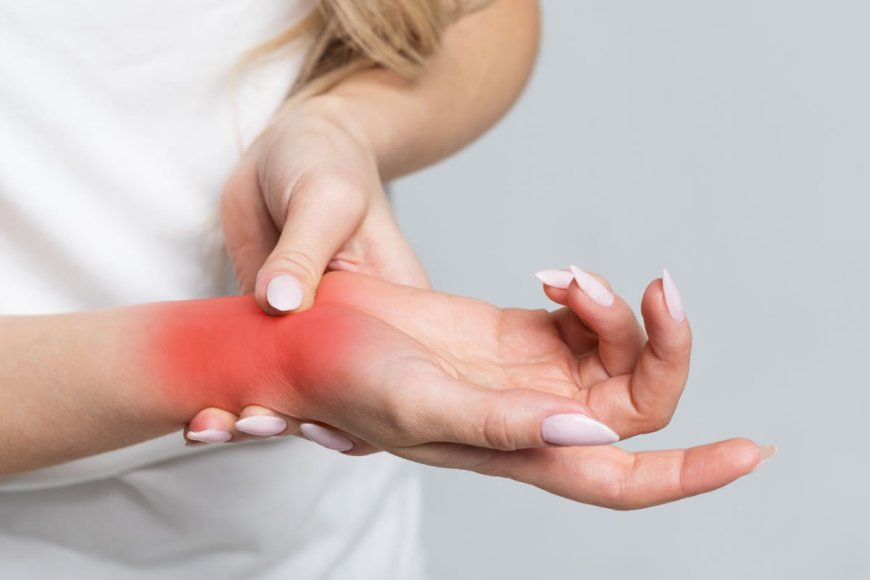
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects the hands and wrists, causing pain, tingling, and weakness. It is important to understand how to prevent CTS to maintain healthy hands, especially in a country like India, where many people engage in repetitive tasks such as typing, using smartphones, or working with hand tools. In this article, we will discuss the signs and symptoms of CTS, its classification, causes, risk factors with examples, types of CTS, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention techniques.
Signs and Symptoms:
The signs and symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome include:
-
Numbness and tingling: You might feel pins and needles in your fingers or hand.
-
Weakness: Your grip may weaken, making it difficult to hold objects.
-
Pain: You may experience pain that radiates from your wrist up to your arm.
-
Nighttime discomfort: The symptoms often worsen at night.
-
Difficulty in fine motor skills: You might struggle with tasks that require precise hand movements, like buttoning a shirt.
Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome means taking measures to keep your hands and wrists healthy. This includes:
-
Taking breaks: If you spend a lot of time doing repetitive tasks, like typing or drawing, take short breaks every hour to rest your hands.
-
Stretching exercises: Regularly perform simple hand and wrist exercises to keep them flexible and reduce strain.
-
Proper posture: Maintain good posture while working to avoid unnecessary strain on your hands and wrists.
-
Ergonomic tools: Use ergonomic keyboards, mice, and other tools that support a natural hand position.
-
Wrist splints: If your doctor recommends it, wearing wrist splints at night can help keep your wrists in a neutral position and reduce pressure on the median nerve.
Causes and Triggers:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from your forearm to your hand through a narrow passage called the carpal tunnel, gets compressed. This compression can be caused by:
-
Repetitive hand movements: Frequent use of the hands in repetitive motions, such as typing or assembly line work, can put pressure on the nerve.
-
Injury or trauma: Fractures or sprains in the wrist can lead to inflammation and compression of the nerve.
-
Health conditions: Conditions like arthritis, diabetes, and thyroid disorders can increase the risk of developing CTS.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain factors increase the risk of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, including:
-
Occupation: People working in jobs that involve repetitive hand movements are more at risk, like office workers who spend long hours typing.
-
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause fluid retention, leading to increased pressure on the median nerve.
-
Obesity: Being overweight can increase the risk of CTS, as excess body weight can contribute to nerve compression.
Types of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
CTS can be classified into two main types:
-
Acute CTS: This type develops suddenly due to an injury or trauma, causing immediate symptoms.
-
Chronic CTS: Chronic CTS develops over time due to repetitive movements or underlying health conditions.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
If you experience symptoms of CTS, a doctor may perform the following diagnostic tests:
-
Physical examination: The doctor will assess your hand, wrist, and arm for signs of CTS.
-
Nerve conduction study: This test measures the speed at which nerves transmit signals and helps identify nerve compression.
-
Electromyogram (EMG): EMG records the electrical activity in muscles and can determine nerve damage.
Treatments for CTS may include:
-
Rest and modification of activities: Avoiding repetitive hand movements can help alleviate symptoms.
-
Pain relievers: Over-the-counter medications may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
-
Corticosteroid injections: These injections can reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief.
-
Physical therapy: Specific exercises can improve wrist strength and flexibility.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, a surgical procedure called carpal tunnel release may be necessary to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
Complications and Prevention:
If left untreated, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can lead to long-term complications, such as permanent nerve damage and loss of hand function. However, early intervention and preventive measures can reduce the risk of complications.
taking care of our hands and wrists is essential in preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. By adopting proper posture, doing hand exercises, and using ergonomic tools, we can keep our hands healthy and avoid the discomfort of CTS. If you experience any symptoms, it's essential to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember, healthy hands lead to a more enjoyable and pain-free life.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0