Palliative Care
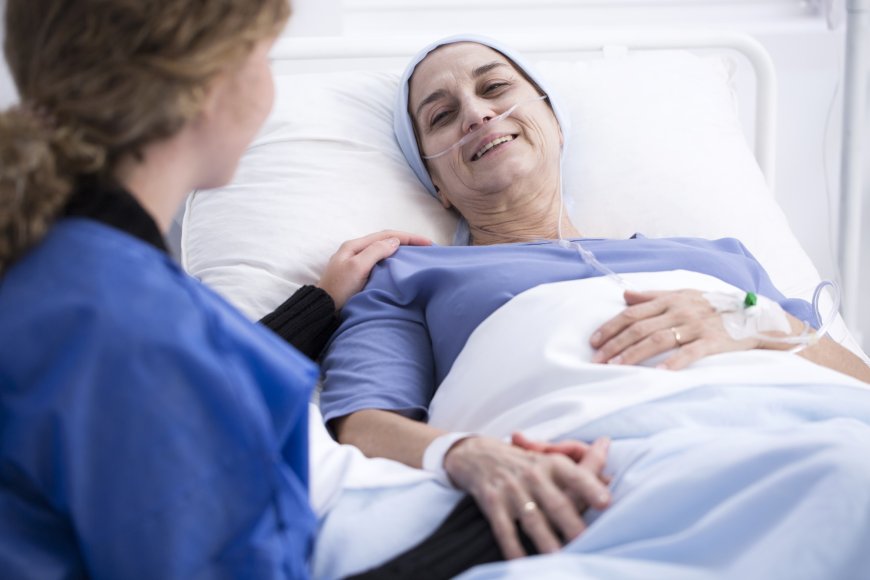

Introduction:
Palliative care is a crucial aspect of healthcare that focuses on improving the quality of life for individuals facing serious illnesses, especially those that are life-threatening or chronic. It aims to provide comfort, pain relief, and emotional support for patients and their families, ensuring that they experience dignity and respect during challenging times. In India, palliative care plays a significant role in addressing the needs of millions of patients with various illnesses.
Signs and Symptoms:
Palliative care is often considered when a person is dealing with severe or long-term medical conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, HIV/AIDS, or other terminal illnesses. Some common signs and symptoms that might indicate the need for palliative care include:
- Persistent pain or discomfort
- Uncontrolled symptoms like nausea or fatigue
- Frequent hospitalizations or ER visits
- Difficulty in performing daily activities
- Emotional distress, anxiety, or depression
- Inability to tolerate treatment side effects
What is Palliative Care?
Palliative care is a specialized form of medical care that focuses on improving the overall quality of life for patients dealing with severe illnesses. It addresses not only physical symptoms but also emotional, psychological, and spiritual aspects of a person's well-being. Palliative care is provided by a team of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, social workers, and counselors, who work together to tailor treatment plans to each patient's unique needs.
How is Palliative Care Classified?
Palliative care can be classified into two primary categories:
-
Primary Palliative Care: This type of care is provided by the primary healthcare team, which includes doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals who are responsible for the patient's overall health and well-being. They integrate palliative care principles into the patient's treatment plan from the early stages of illness.
-
Specialized Palliative Care: This form of care is provided by a team of specialized healthcare professionals who have extensive training and experience in managing complex symptoms and addressing the emotional and psychological needs of patients. They work collaboratively with the primary care team to offer comprehensive support.
Causes and Triggers:
Palliative care is usually recommended for patients dealing with serious, life-limiting, or chronic illnesses. Some common causes and triggers for considering palliative care include:
-
Cancer: Patients undergoing cancer treatment may experience severe pain, nausea, or emotional distress, making palliative care essential in managing these symptoms.
-
Heart Disease: Individuals with advanced heart conditions may struggle with shortness of breath, fatigue, and anxiety, all of which palliative care can help alleviate.
-
Neurological Disorders: Patients with conditions like multiple sclerosis or motor neuron diseases may require palliative care to manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.
-
HIV/AIDS: Palliative care plays a crucial role in providing comfort and support to patients with advanced HIV/AIDS, addressing symptoms and psychological well-being.
Risk Factors with Examples:
The need for palliative care is not limited to any specific age group, and various risk factors may indicate its necessity. For instance:
-
Age: Elderly individuals may need palliative care as they are more susceptible to chronic illnesses like heart disease and cancer.
-
Chronic Illness: Patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes or kidney disease may benefit from palliative care to manage symptoms effectively.
-
Terminal Illness: Individuals diagnosed with terminal illnesses like advanced-stage cancer may require palliative care to enhance their quality of life during treatment.
Types of Palliative Care:
-
Pain Management: This type of care focuses on addressing and alleviating pain through medications, physical therapy, and other pain relief techniques.
-
Emotional Support: Palliative care also includes counseling and emotional support to help patients and their families cope with the challenges of their illnesses.
-
Symptom Management: Managing symptoms like nausea, fatigue, and breathing difficulties is an essential aspect of palliative care, helping patients feel more comfortable and in control.
-
Spiritual Support: Palliative care recognizes the importance of spiritual well-being, and chaplains or counselors may be involved to offer spiritual support to patients and families.
-
End-of-life Care: Palliative care extends to end-of-life care, ensuring that patients' final days are spent with dignity and respect, surrounded by loved ones.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
-
Pain Assessment: Doctors use various tools to assess a patient's pain level, such as the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) or Faces Pain Scale, to determine the most suitable pain management plan.
-
Medication Management: Palliative care specialists prescribe medications like opioids, antidepressants, or anti-nausea drugs to manage symptoms effectively.
-
Counseling and Therapy: Psychological therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) may be used to help patients cope with emotional distress and anxiety.
-
Physiotherapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to improve mobility and manage symptoms like muscle pain or weakness.
Complications of Palliative Care:
Palliative care is designed to minimize complications and improve a patient's overall well-being. However, some potential challenges include:
-
Medication Side Effects: Some medications used for symptom management may have side effects that need careful monitoring.
-
Emotional Impact: Patients and families may experience emotional challenges as they confront the realities of a severe illness.
-
Communication Issues: Effective communication among the patient, family, and healthcare team is essential to ensure all needs are met.
Prevention Techniques:
While palliative care focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of preventive healthcare measures. Regular medical check-ups, healthy lifestyle choices, and disease prevention strategies can reduce the risk of severe illnesses and enhance overall well-being.
Palliative care is a compassionate and essential form of medical care that supports patients and their families through challenging times. It ensures that individuals facing serious illnesses receive the comfort, relief, and emotional support they need to lead a dignified and meaningful life. By combining expert medical care with emotional and spiritual support, palliative care plays a vital role in improving the overall quality of life for patients in India and around the world.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0