Knee Replacement Surgery
Introduction:
In India, just like anywhere else in the world, people may experience knee pain and mobility issues due to various reasons. When knee problems become severe and affect daily activities, doctors may recommend knee replacement surgery as an effective solution to restore mobility and alleviate pain. Let's explore knee replacement surgery, its signs, symptoms, different types, causes, risk factors, diagnostic tests, treatments, and preventive measures in simple language, so even 10-year-old children can easily understand.
Signs and Symptoms:
Knee problems may manifest in different ways, including:
- Pain and stiffness in the knee, even while resting.
- Difficulty in walking or climbing stairs.
- Swelling and tenderness around the knee joint.
- A decrease in knee flexibility.
- Feeling of instability or weakness in the knee.
What Is Knee Replacement Surgery?
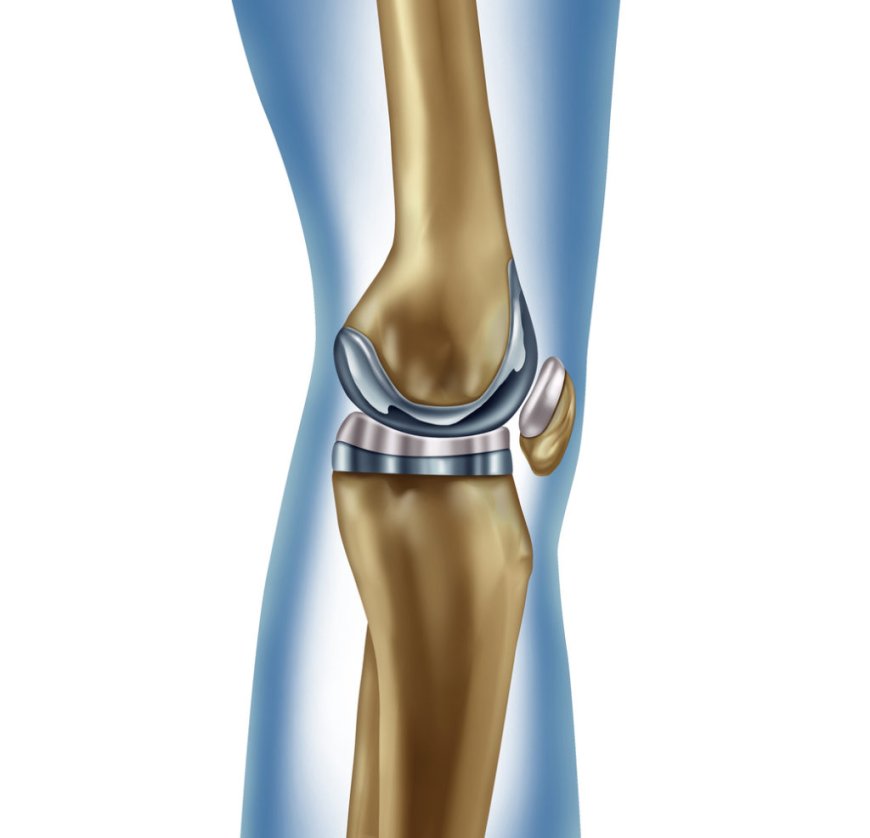
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a medical procedure where a damaged knee joint is replaced with an artificial joint called a prosthesis. The prosthesis is designed to function and move like a real knee joint, providing relief from pain and improved mobility.
How Is Knee Replacement Surgery Classified?
Knee replacement surgery is classified into two main types:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): In this surgery, both the damaged ends of the thigh bone and shin bone are replaced with artificial components.
- Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): When only one part of the knee joint is affected, such as the inner or outer knee, only that portion is replaced with a prosthesis.
Causes and Triggers:
Knee problems can be caused by several factors, including:
- Osteoarthritis: A condition where the protective cartilage that cushions the knee joint wears away over time.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the knee joint.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Occurs after a knee injury or fracture that doesn't heal properly.
- Knee Deformities: Abnormalities in the knee structure present from birth or developed over time.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing knee problems, such as:
- Age: As people get older, the risk of knee issues like osteoarthritis increases.
- Obesity: Carrying excess weight puts more pressure on the knee joints, leading to wear and tear.
- Sports Injuries: Activities like football, basketball, or dancing may lead to knee injuries and subsequent problems.
- Family History: If someone in the family has knee issues, there might be a genetic predisposition to such problems.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery:
a) Total Knee Replacement (TKR): In TKR, the surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone from the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia). Then, they replace them with metal and plastic components that form the new knee joint.
b) Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): In PKR, only the affected part of the knee joint is replaced with a prosthesis, leaving the healthy portions intact. This is suitable for patients with limited knee damage.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
a) X-rays: X-rays use radiation to create images of the knee, helping doctors see the extent of damage and decide if surgery is necessary.
b) MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of the knee's soft tissues, allowing doctors to diagnose issues like ligament tears.
Complications and Prevention Techniques:
Knee replacement surgery, like any major surgery, comes with risks such as infection, blood clots, or implant loosening. To prevent complications, doctors may advise:
-
Pre-surgery evaluation: Ensuring the patient is healthy enough for surgery and addressing any underlying conditions.
-
Post-surgery care: Following the doctor's instructions for medication, physical therapy, and rehabilitation.
-
Maintaining a healthy weight: Reducing the pressure on the knee joint can minimize complications.
Knee replacement surgery is a transformative procedure that has helped countless people in India and around the world regain their mobility and live pain-free lives. By understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, and preventive measures, individuals can take better care of their knees and potentially avoid the need for surgery. Remember, always consult a doctor for personalized advice and treatment options.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0