knee Pain
Introduction:
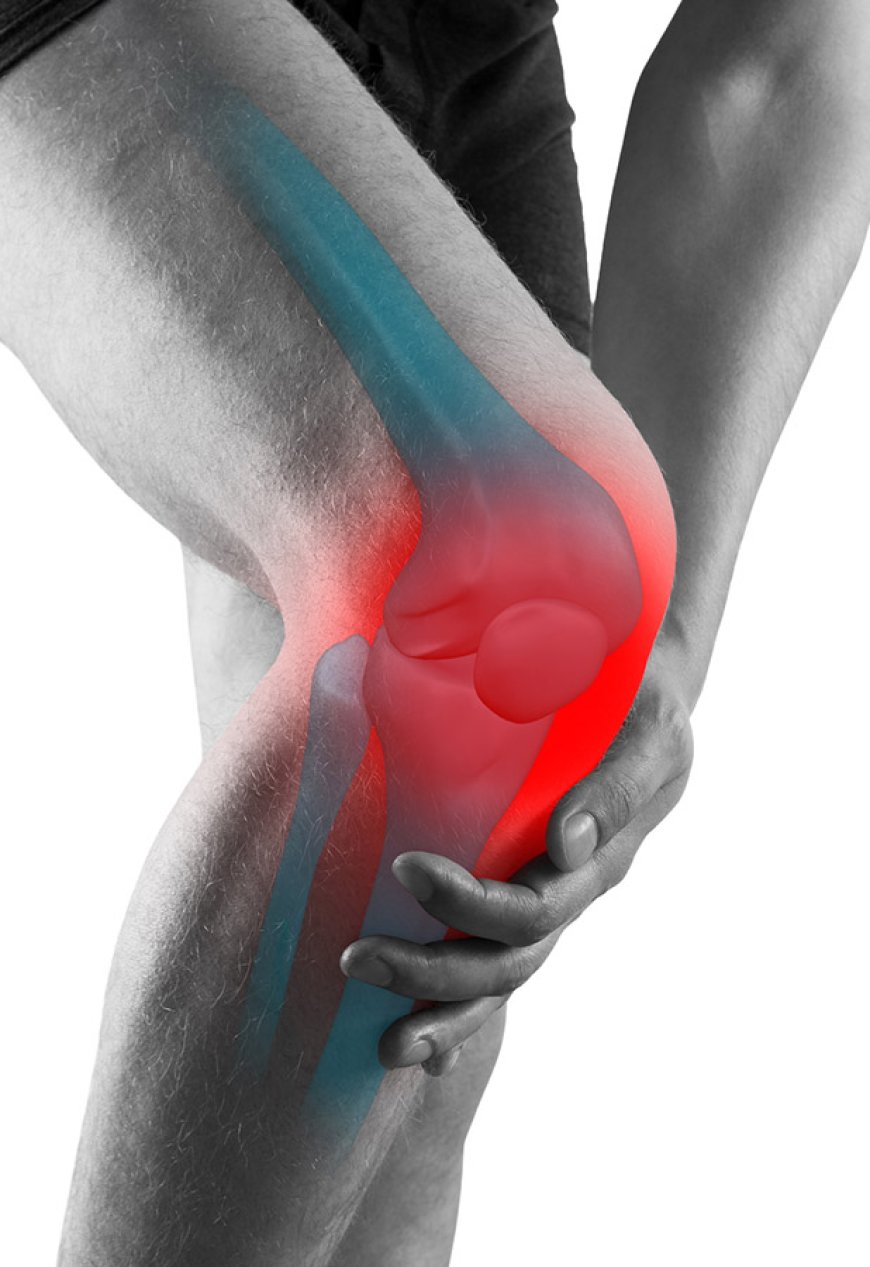
Knee pain is a prevalent health issue affecting people of all ages in India. The knee joint plays a crucial role in our daily activities, such as walking, running, and climbing stairs. However, due to various factors, knee pain can arise, making it challenging to perform these simple tasks. In this article, we will explore the signs and symptoms, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention techniques related to knee pain in India.
Signs and Symptoms:
Knee pain can present itself in several ways, and the symptoms may vary from person to person. Some common signs and symptoms include:
-
Pain: Aching, sharp, or dull pain in the knee joint, which may worsen with movement or prolonged sitting or standing.
-
Swelling: The knee may become swollen, making it difficult to bend or straighten the leg.
-
Stiffness: The knee may feel stiff, making it hard to move freely.
-
Redness and warmth: The knee area may appear red and feel warm to the touch.
-
Clicking or popping sounds: Some people may experience clicking or popping sensations when moving their knee.
What Is Knee Pain?
Knee pain is a discomfort or ache experienced in the knee joint, which can be caused by various underlying factors. It can occur suddenly due to an injury or gradually due to wear and tear over time.
How Is Knee Pain Classified?
Knee pain can be classified based on the location and severity of the discomfort. It can be broadly categorized into three types:
-
Acute Knee Pain: This type of pain occurs suddenly and is often the result of an injury or trauma, such as a fall, sports-related accident, or sudden twist of the knee.
-
Chronic Knee Pain: Chronic knee pain is long-lasting and develops gradually over time. It is commonly associated with conditions like arthritis, tendinitis, or cartilage degeneration.
-
Overuse Knee Pain: Overuse knee pain occurs due to repetitive stress on the knee joint. Activities such as running, jumping, or excessive kneeling can lead to this type of pain.
Causes and Triggers:
Various factors can contribute to knee pain in India, including:
-
Osteoarthritis: A common cause of knee pain, especially among older adults. It involves the gradual breakdown of the joint's cartilage.
-
Injuries: Sports-related injuries, falls, or accidents can damage the ligaments, tendons, or meniscus in the knee.
-
Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional stress on the knee joint, leading to pain and discomfort.
-
Lack of Exercise: Insufficient physical activity can weaken the muscles around the knee, making it more prone to injuries.
-
Poor Posture: Incorrect posture while walking or sitting can strain the knee joint.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing knee pain. Some examples include:
-
Age: As people age, the risk of knee pain, especially from conditions like osteoarthritis, increases.
-
Sports Participation: Active individuals who engage in high-impact sports, like football or basketball, have a higher risk of knee injuries.
-
Occupational Hazards: Jobs that involve prolonged standing, heavy lifting, or repetitive knee movements can increase the risk of knee pain.
Types of Knee Pain:
-
Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease that leads to the breakdown of cartilage in the knee.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks the joints, leading to inflammation and pain.
-
Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons that connect muscles to the knee bones.
-
Meniscus Tear: A tear in the cartilage discs (menisci) that act as shock absorbers in the knee.
-
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Pain around the kneecap caused by improper tracking of the kneecap.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
To diagnose knee pain accurately and determine the appropriate treatment, doctors may use the following diagnostic tests:
-
X-rays: To visualize the bones and detect any signs of arthritis or fractures.
-
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): To get detailed images of soft tissues like ligaments and cartilage.
-
Ultrasound: To assess soft tissue injuries, swelling, or fluid accumulation in the knee.
-
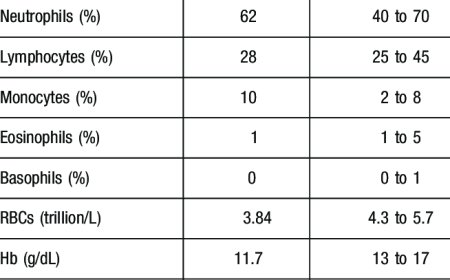
Blood Tests: To check for markers of inflammation and certain autoimmune conditions.
Treatment options for knee pain may include:
-
Rest and Ice: Resting the knee and applying ice can reduce inflammation and pain.
-
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises can strengthen the knee muscles and improve flexibility.
-
Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
-
Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections can provide temporary relief for certain conditions.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, surgical procedures like knee replacement or arthroscopy may be recommended.
Complications of Knee Pain:
Untreated knee pain can lead to complications such as chronic discomfort, limited mobility, and difficulty performing daily activities.
Prevention Techniques:
To prevent knee pain, consider the following:
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts strain on the knee joint, so maintaining a healthy weight is essential.
-
Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to strengthen the knee muscles.
-
Proper Posture: Maintain good posture while sitting, standing, and walking to reduce strain on the knee.
-
Warm-up: Always warm up before exercising or playing sports to prevent injuries.
Knee pain is a common issue in India that can affect people of all ages. By understanding the signs, causes, and preventive measures, individuals can take steps to manage or avoid knee pain, ensuring a healthier and more active life. Remember to seek medical advice promptly if you experience persistent or severe knee pain to receive proper diagnosis and treatment.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0