Kawasaki disease
Introduction:
Kawasaki disease is a rare but serious illness that primarily affects children, and it has been a topic of concern in India as well. First identified by a Japanese doctor, Dr. Tomisaku Kawasaki, in 1967, this disease has puzzled scientists and medical experts for years. In this article, we will delve into the signs and symptoms, classification, causes and triggers, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention techniques of Kawasaki disease, making it easy for young minds to grasp.
Signs and Symptoms:
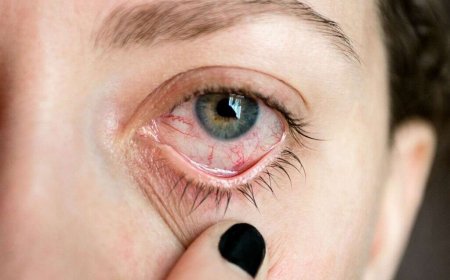
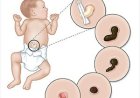
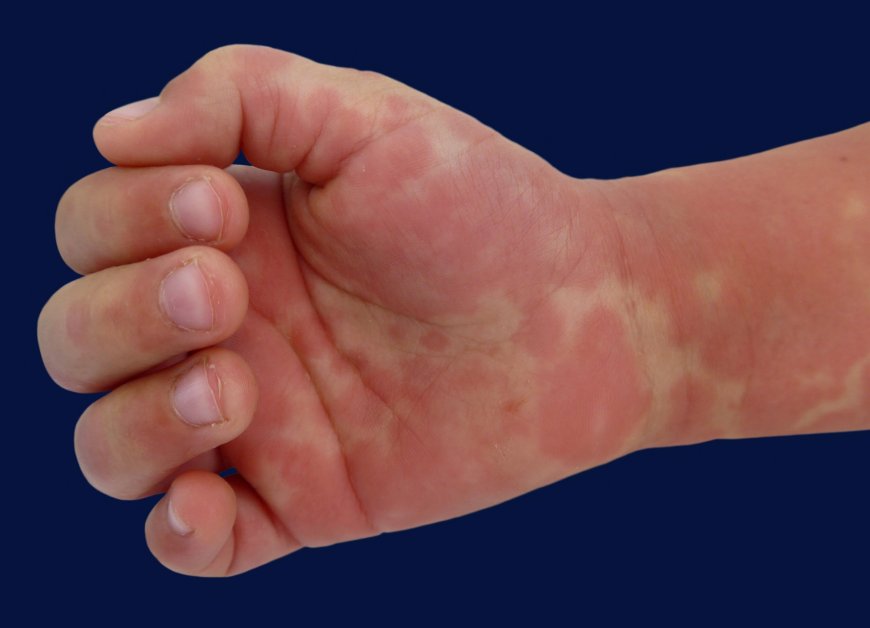
Kawasaki disease often begins with a high fever that persists for several days and is accompanied by various symptoms, such as red eyes, dry and cracked lips, a strawberry-like tongue, and swollen lymph nodes in the neck. Additionally, a rash may appear on the body, especially in the genital area, palms, and soles of the feet. Some children may experience joint pain, abdominal discomfort, and peeling of the skin on the hands and feet during the later stages of the disease.
What Is Kawasaki Disease?
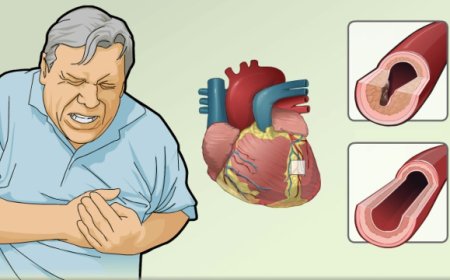
Kawasaki disease is an inflammatory condition that primarily affects the blood vessels throughout the body, including the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. If not treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications, such as heart problems.
How Is Kawasaki Disease Classified?
Kawasaki disease is classified into two types based on the duration of fever. The typical or classic Kawasaki disease presents with a fever that lasts for at least five days. The incomplete or atypical Kawasaki disease features some symptoms of the disease but with a shorter fever duration.
Causes and Triggers:
The exact cause of Kawasaki disease remains unknown, but experts believe it may be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some theories suggest that viral or bacterial infections could be potential triggers, but no specific pathogen has been identified as the primary cause.
Risk Factors:
While Kawasaki disease can affect any child, certain factors increase the risk of developing the disease. For example, it is more common in children under the age of five, especially in those of Asian descent. However, cases have been reported in children of various ethnic backgrounds. Let's meet two children from India to understand the risk factors better:
-
Arjun (5 years old): Arjun, a young boy from Delhi, was recently diagnosed with Kawasaki disease. He is of Indian descent and fits the typical age group susceptible to the disease.
-
Ayesha (3 years old): Ayesha, a girl from Mumbai, comes from a mixed-race background. Despite not being of Asian descent, she also contracted Kawasaki disease, proving that it can affect children from diverse ethnicities.
Types of Kawasaki Disease:
As mentioned earlier, Kawasaki disease is classified into two types: typical and incomplete. The typical form represents the full-blown manifestation of the disease with a prolonged fever, while the incomplete type presents with some but not all characteristic symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
Diagnosing Kawasaki disease involves a combination of clinical observations and laboratory tests. The following diagnostic tests are commonly used:
-
Physical Examination: Doctors examine the child for signs of inflammation and check for the classic symptoms of Kawasaki disease.
-
Blood Tests: Blood tests help in assessing inflammation markers, such as elevated white blood cell count and C-reactive protein levels.
-
Echocardiogram: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to produce images of the heart and is crucial for detecting potential heart complications.
Treatments:
-
Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG): The main treatment for Kawasaki disease is administering IVIG, which is a concentrated mixture of antibodies that helps reduce inflammation and prevent heart-related complications.
-
Aspirin: High-dose aspirin is given to reduce fever and inflammation, but the dose is adjusted later to prevent a rare but serious condition called Reye's syndrome.
Complications of Kawasaki Disease:
When diagnosed and treated early, Kawasaki disease often resolves without long-term consequences. However, if left untreated or if complications arise, it can lead to damage to the heart, potentially causing coronary artery aneurysms or other heart-related problems.
Prevention Techniques:
As the exact cause of Kawasaki disease remains unknown, there are no specific preventive measures. However, recognizing the early signs and seeking medical attention promptly can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Kawasaki disease remains a medical mystery, but with ongoing research and awareness, we hope to find more answers and better ways to manage this condition. Parents, teachers, and children themselves should be vigilant about recognizing the signs and symptoms to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment. Together, we can work towards protecting our little ones and their hearts, making India and the world a healthier place for children to grow and thrive.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0