Home Blood sugar monitoring
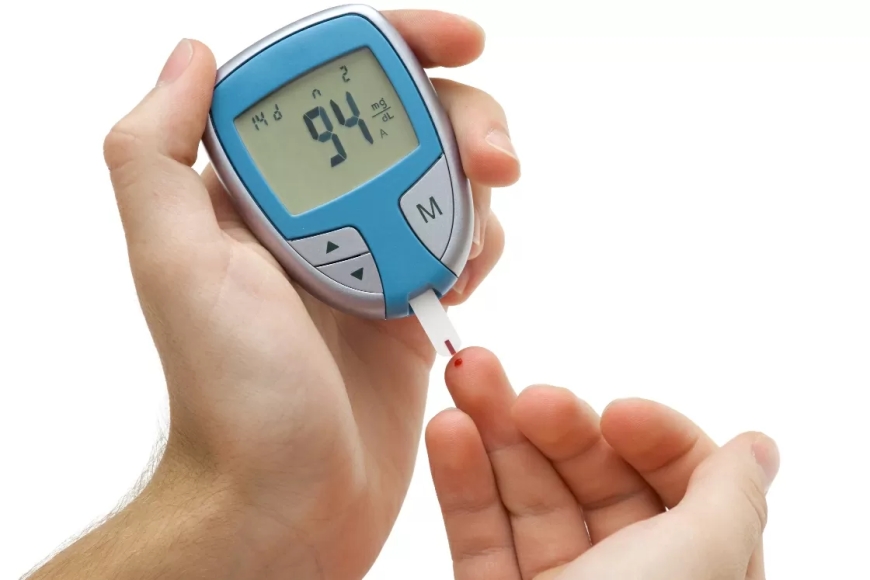
Introduction:
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide, including in India. It is essential for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly to manage their condition effectively and lead a healthy life. Home blood sugar monitoring plays a vital role in helping people with diabetes keep their blood sugar levels in check. In this article, we will explore the importance of home blood sugar monitoring, its classification, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention techniques, all explained in simple language for 10-year-old children to understand.
Signs and Symptoms:
When someone has high blood sugar levels, they may experience symptoms such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, increased hunger, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. On the other hand, low blood sugar levels can cause symptoms like shakiness, sweating, confusion, dizziness, and irritability.
What is Home Blood Sugar Monitoring?
Home blood sugar monitoring is a method by which individuals with diabetes can check their blood sugar levels from the comfort of their homes. It involves using a small device called a glucometer, which measures blood sugar levels through a tiny drop of blood obtained by pricking the fingertip.
Classification of Home Blood Sugar Monitoring:
Home blood sugar monitoring can be classified into two types:
-
Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): This is the most common type, where individuals check their blood sugar levels multiple times a day using a glucometer. It helps them understand how their blood sugar levels change throughout the day based on their activities and meals.
-
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGM is a newer technology that involves wearing a small sensor under the skin, which continuously measures blood sugar levels. It provides real-time data and trends to help individuals make better decisions about their diet and insulin doses.
Causes and Triggers:
Diabetes occurs when the body cannot properly use or produce insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. In Type 2 diabetes, the body becomes insulin resistant, and the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to meet the body's demands.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Several factors can increase the risk of developing diabetes in India. Some common risk factors include:
-
Family History: If someone has close relatives, like parents or siblings, with diabetes, they have a higher risk.
-
Unhealthy Diet: Consuming sugary drinks, processed foods, and unhealthy snacks can contribute to diabetes risk.
-
Lack of Physical Activity: Being inactive or not engaging in regular exercise can increase the risk of diabetes.
-
Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for diabetes.
-
Age: As people get older, the risk of diabetes increases. For example, people over 45 years are more susceptible to Type 2 diabetes.
Types of Home Blood Sugar Monitoring:
-
SMBG (Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose): As mentioned earlier, SMBG involves pricking the fingertip to get a drop of blood and using a glucometer to check blood sugar levels. This method is affordable, convenient, and widely accessible.
-
CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitoring): CGM uses a sensor placed under the skin to measure blood sugar levels continuously. It provides real-time data and can alert the individual if their blood sugar is too high or too low.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
Diagnosing diabetes involves testing blood sugar levels through various diagnostic tests:
-
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test (FPG): This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. A level higher than 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) indicates diabetes.
-
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): In this test, the person drinks a glucose-rich solution, and blood sugar levels are tested at different intervals. A blood sugar level above 200 mg/dL after two hours indicates diabetes.
-
Hemoglobin A1c Test (HbA1c): This test measures the average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. An HbA1c level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes.
Treatments for Diabetes:
The primary treatments for diabetes include:
-
Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight can help manage diabetes.
-
Medication: Some individuals may require medications like insulin or oral diabetes medications to control blood sugar levels effectively.
-
Insulin Pump: For some, an insulin pump is an option. It continuously delivers insulin to the body, providing better control.
Complications of Home Blood Sugar Monitoring:
If blood sugar levels are not properly managed, diabetes can lead to various complications, such as:
-
Cardiovascular Problems: Diabetes can increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases.
-
Nerve Damage: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and tingling in the hands and feet.
-
Kidney Damage: Diabetes can cause kidney damage, leading to kidney failure in severe cases.
-
Eye Problems: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems and even blindness.
Prevention Techniques:
Preventing diabetes involves adopting a healthy lifestyle:
-
Balanced Diet: Eat a variety of nutritious foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
-
Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, such as playing sports, dancing, or cycling.
-
Limit Sugary Drinks: Avoid consuming sugary beverages like sodas and energy drinks.
-
Regular Check-ups: Visit the doctor regularly for health check-ups to detect and manage diabetes early.
Home blood sugar monitoring is a crucial tool in managing diabetes effectively. By regularly monitoring blood sugar levels, making necessary lifestyle changes, and following medical advice, individuals with diabetes in India can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Remember, diabetes is manageable, and with the right knowledge and support, anyone can take control of their health and well-being.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0