DIABETES DURING PREGNANCY

Introduction:
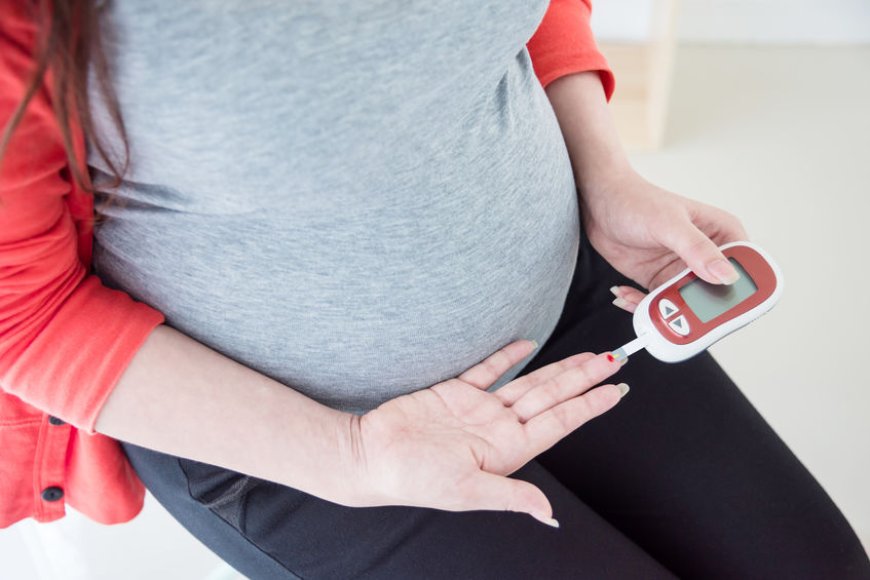
Diabetes during pregnancy, also known as gestational diabetes, is a condition that affects pregnant women in India and around the world. It is essential to recognize the signs, understand the different types, causes, and risk factors, and learn about the diagnostic tests and treatment options to ensure a healthy pregnancy for both the mother and the baby.
Signs and Symptoms:
The signs of diabetes during pregnancy are often subtle and can be mistaken for typical pregnancy symptoms. These may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, and recurrent infections. Sometimes, pregnant women may not experience any noticeable symptoms, which is why regular check-ups are crucial.
What is Diabetes During Pregnancy?
Diabetes during pregnancy occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. As a result, sugar accumulates in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels, which can be harmful to both the mother and the baby.
Classification of Diabetes During Pregnancy:
Diabetes during pregnancy is classified into two main types:
-
Gestational Diabetes: This type of diabetes develops during pregnancy and usually goes away after childbirth. It affects around 7% of pregnant women in India.
-
Pre-existing Diabetes: Some women may have diabetes before becoming pregnant. If they do, it can continue during pregnancy and require special care.
Causes and Triggers:
The exact cause of gestational diabetes is not entirely understood, but some factors can contribute to its development. These may include a family history of diabetes, being overweight or obese, and a sedentary lifestyle. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also affect insulin production and action, increasing the risk of gestational diabetes.
Risk Factors:
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing diabetes during pregnancy. These include:
- Age: Women over 25 are at higher risk.
- Family History: Having a family member with diabetes increases the risk.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese raises the risk significantly.
- Previous Gestational Diabetes: Women who had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy are more likely to develop it again.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS are at an increased risk.
- Ethnicity: Women of South Asian, Indian, or Hispanic descent have a higher risk.
Types of Diabetes During Pregnancy:
There are two main types of diabetes that pregnant women may experience:
-
Gestational Diabetes: As mentioned earlier, this type occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth.
-
Pre-existing Diabetes: This type includes both Type 1 diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin, and Type 2 diabetes, where the body does not use insulin properly. Women with pre-existing diabetes should carefully manage their blood sugar levels during pregnancy to prevent complications.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
To detect diabetes during pregnancy, doctors use the following tests:
-
Glucose Challenge Test (GCT): This is an initial screening test where the pregnant woman drinks a sugary solution, and blood sugar levels are measured after an hour.
-
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): If the GCT indicates high blood sugar levels, an OGTT is performed. It involves fasting overnight, followed by drinking a more concentrated sugary solution. Blood sugar levels are tested before and after one, two, and three hours to diagnose gestational diabetes.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for gestational diabetes aims to keep blood sugar levels in a healthy range. It includes:
-
Dietary Changes: A balanced diet with controlled carbohydrate intake helps manage blood sugar levels.
-
Regular Exercise: Engaging in safe physical activities can help improve insulin sensitivity.
-
Insulin Injections: In some cases, insulin injections may be required to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Complications and Prevention:
Unmanaged diabetes during pregnancy can lead to several complications, such as:
-
Macrosomia: The baby may be born larger than usual, making delivery more complicated.
-
Hypoglycemia: After birth, the baby's blood sugar levels may drop, requiring medical attention.
-
Pre-eclampsia: High blood pressure during pregnancy can lead to pre-eclampsia, which is dangerous for both mother and baby.
Prevention techniques include maintaining a healthy weight before pregnancy, adopting a balanced diet and exercise routine, and attending regular prenatal check-ups to monitor blood sugar levels.
Diabetes during pregnancy is a condition that requires careful management and regular medical supervision. With the right care and attention, pregnant women with diabetes can have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a happy, healthy baby. Early detection, proper treatment, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are essential in ensuring a positive outcome for both mother and child.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0