Dehydration
Introduction:
Dehydration is a common condition that occurs when our body loses more water than it takes in. In India, a diverse country with varying climates, dehydration can be a serious health concern, especially during scorching summers or in regions with limited access to clean water. Let's explore what dehydration is, its symptoms, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention techniques in simple language that even 10-year-old children can understand.
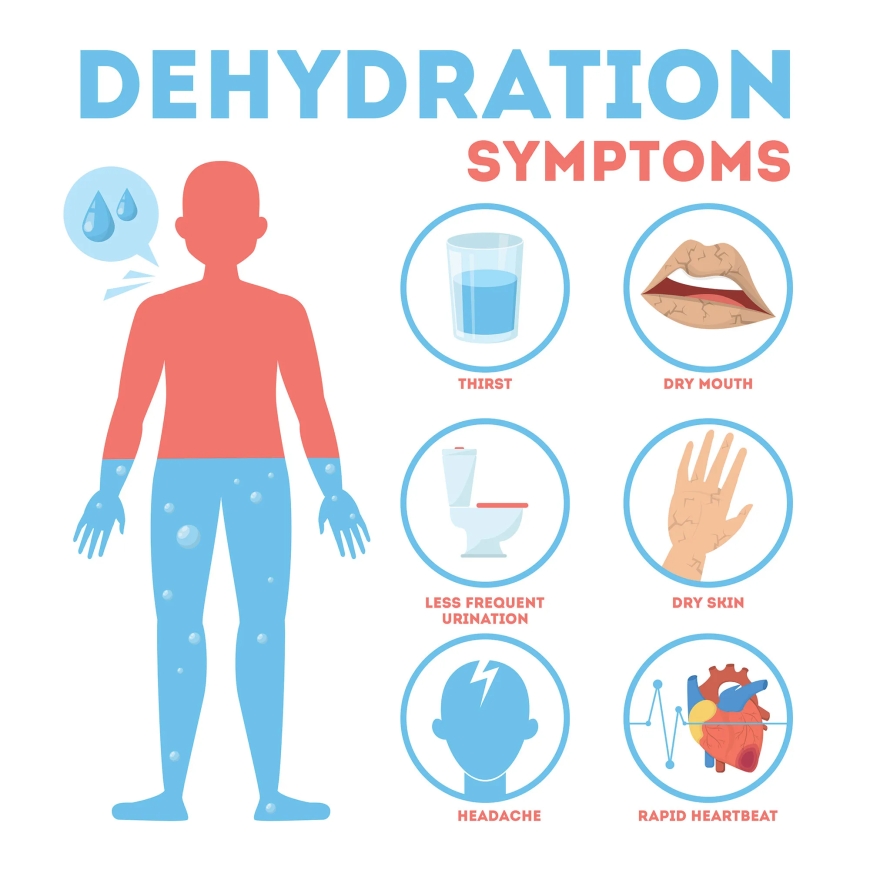
Signs and Symptoms:
Dehydration shows various signs and symptoms, such as feeling thirsty, having a dry mouth, tiredness, dark yellow urine, and dry skin. In severe cases, dehydration can lead to dizziness, confusion, rapid heartbeat, and fainting.
What Is Dehydration?
Dehydration happens when our body loses more water and essential salts (like sodium, potassium, and chloride) than it needs to function properly. Water is essential for our body to carry out its functions effectively, such as regulating body temperature, aiding digestion, and transporting nutrients.
How Is Dehydration Classified?
Dehydration can be classified into three types based on the severity:
-
Mild Dehydration: When the body loses only a small amount of water, and the symptoms are not severe. Drinking more fluids can usually help with mild dehydration.
-
Moderate Dehydration: When the body loses a significant amount of water and essential salts. Medical attention and oral rehydration solutions may be required.
-
Severe Dehydration: This is a critical condition where the body loses a large amount of water and essential salts. Immediate medical attention and intravenous (IV) fluids are necessary to prevent complications.
Causes and Triggers:
Dehydration can be caused by various factors, including:
- Not drinking enough water, especially during hot weather or physical activity.
- Excessive sweating without adequate fluid intake.
- Diarrhea or vomiting, which leads to significant water loss.
- Fever, which increases the body's water requirements.
- Certain medical conditions like diabetes or kidney problems can contribute to dehydration.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain people are more prone to dehydration due to various reasons. Here are some risk factors:
-
Children and older adults: Their bodies may not signal thirst as effectively, leading to inadequate water intake.
-
Athletes: Engaging in intense physical activities without sufficient fluid intake can cause dehydration.
-
People with chronic illnesses: Conditions like diabetes can increase the risk of dehydration.
Types of Dehydration with Detailing for Each Type:
There are two primary types of dehydration:
-
Hypertonic Dehydration: This type occurs when the body loses more water than salt, leading to an imbalance in the body's fluids. It commonly happens with intense physical activity or in hot climates.
-
Hypotonic Dehydration: Here, the body loses more salt than water, causing an imbalance in electrolytes. It can occur with prolonged vomiting or diarrhea.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
To diagnose dehydration, doctors may perform the following tests:
-
Physical Examination: The doctor will check for signs like dry mouth, low blood pressure, and rapid heartbeat.
-
Blood Tests: These tests can measure the levels of electrolytes and determine the severity of dehydration.
-
Urinalysis: A urine sample can help assess dehydration levels.
Treatments for dehydration may include:
-
Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS): For mild to moderate dehydration, drinking ORS can help replenish lost fluids and electrolytes.
-
Intravenous (IV) Fluids: In severe cases, where oral intake is not possible, fluids are administered directly into the veins.
Complications of Dehydration and Prevention Techniques:
Severe dehydration can lead to dangerous complications like kidney problems, heatstroke, and even life-threatening situations. To prevent dehydration:
-
Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during hot weather or physical activities.
-
Consume hydrating foods like watermelon, cucumber, and oranges.
-
Avoid sugary or caffeinated drinks, as they can worsen dehydration.
-
Seek shade and avoid excessive physical exertion during hot days.
In India, dehydration is a serious concern, especially in regions with hot climates and limited access to clean water. It's essential to stay hydrated and recognize the signs of dehydration to prevent complications. By drinking enough water, eating hydrating foods, and taking necessary precautions, we can maintain a healthy water balance and keep ourselves safe from dehydration's harmful effects.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0