Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Introduction:
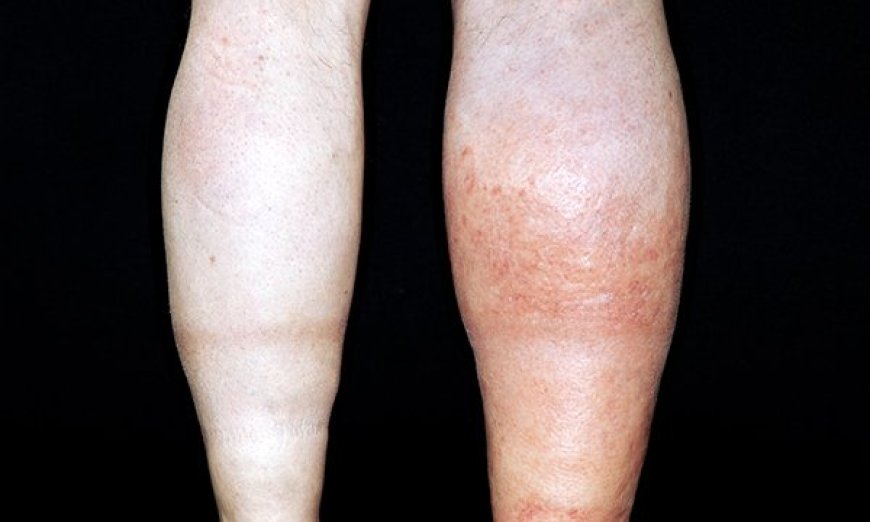
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that can affect people of all ages, including children in India. It occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. This article aims to explain DVT in simple language, making it easy for 10-year-old children to understand.
Signs and Symptoms:
When someone has DVT, they might experience symptoms like swelling, pain, and tenderness in one leg. The skin over the affected area might feel warm or look reddish or bluish. Sometimes, children with DVT may have difficulty walking or complain of their legs feeling heavy.
What Is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep Vein Thrombosis, also known as DVT, is a condition where a blood clot forms inside a deep vein. Veins are like tubes that carry blood back to our heart. When a clot forms in these veins, it can block blood flow and cause problems.
How Is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Classified?
DVT can be classified based on how it happens and where it occurs:
-
Acquired DVT: This happens when something specific triggers the formation of a clot, like an injury, surgery, or prolonged sitting during a long journey.
-
Congenital DVT: Sometimes, children are born with a higher risk of getting DVT because of certain genetic factors.
Causes and Triggers:
DVT can be caused by different things. Sometimes, it occurs without any clear reason, but other times, certain factors can trigger it. Some common triggers are:
-
Injury: When a child hurts their leg, it can cause a clot to form.
-
Surgery: Certain surgeries can increase the risk of DVT because it can make blood flow slower.
-
Immobility: When someone has to stay in bed for a long time, like after an illness, the blood can pool and form a clot.
-
Family History: If someone in the family has had DVT, it might increase the risk for other family members too.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain things can make someone more likely to get DVT. Here are some risk factors with examples:
-
Obesity: Being overweight can put extra pressure on the veins.
-
Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels, making it easier for clots to form.
-
Medications: Some medicines might increase the risk of clotting.
-
Age: Older people are at higher risk.
Types of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) with Detailing for Each Type:
DVT can occur in different parts of the body. The two main types are:
-
Lower Extremity DVT: This type occurs in the legs, usually in the thigh or calf. It's the most common type in both adults and children.
-
Upper Extremity DVT: This type occurs in the arms and is less common.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
If a doctor suspects DVT, they will use some tests to confirm it. Here are the common tests:
-
Ultrasound: This uses sound waves to create pictures of the veins and check for clots.
-
Blood Tests: Doctors might check for substances in the blood that could suggest a clot.
-
Venography: A special dye is injected into the veins, and X-rays are taken to see the blood flow.
Treatments for DVT may include:
-
Blood Thinners: These medicines help prevent new clots from forming and stop existing ones from growing.
-
Compression Stockings: These are special stockings that put pressure on the legs to help blood flow better.
-
Thrombolytic Therapy: In severe cases, medicines are given to dissolve the clot.
Complications of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Prevention Techniques:
If not treated, DVT can lead to serious problems like a pulmonary embolism, where a piece of the clot breaks off and travels to the lungs. To prevent DVT, it's essential to:
-
Stay Active: Regular exercise helps keep blood flowing.
-
Avoid Sitting or Standing for Too Long: Take breaks and stretch your legs if sitting or standing for long periods.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water keeps the blood from thickening too much.
Deep Vein Thrombosis can be a serious condition, but with awareness and early treatment, it can be managed effectively. Remember to always tell an adult if you notice any signs of DVT in yourself or others. Stay active, eat healthy, and take care of your body to reduce the risk of DVT.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0