Breast Pain (Mastalgia)

Introduction:
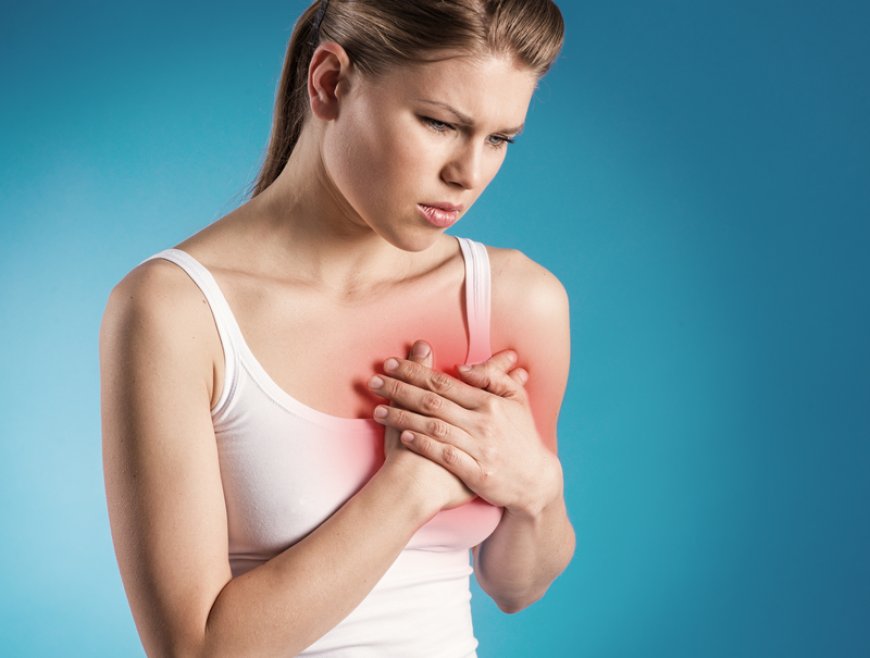
Breast pain, also known as mastalgia, is a common concern for many people, including women, in India. It refers to discomfort, tenderness, or pain in the breasts that can occur at different times and with various degrees of intensity. In this article, we will explore breast pain in the Indian context, discussing its signs and symptoms, classifications, causes, risk factors with examples, types, diagnostic tests, treatments, complications, and prevention techniques. Additionally, we will learn about notable public figures in India who have experienced breast pain.
Signs and Symptoms:
Breast pain can present itself in different ways. Some common signs and symptoms of mastalgia include:
- Tenderness or sensitivity in the breasts
- Dull, achy, or sharp pain in one or both breasts
- Pain that fluctuates with the menstrual cycle
- Pain during physical activities or when pressure is applied to the breasts
- Swelling or lumps in the breast tissue (note: not all breast lumps are related to cancer)
What is Breast Pain (Mastalgia)? :
Breast pain or mastalgia is a discomfort experienced in the breast area. It is essential to remember that mastalgia is not a disease but rather a symptom that can be caused by various underlying factors.
How is Breast Pain (Mastalgia) Classified?:
Breast pain can be classified based on when it occurs and its relationship to the menstrual cycle. There are two primary types of mastalgia:
-
Cyclical Mastalgia: This type of breast pain is associated with hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle. It usually occurs in both breasts and is more common in younger women.
-
Non-Cyclical Mastalgia: Non-cyclical breast pain does not follow any specific pattern related to the menstrual cycle. It can occur in one or both breasts and is more common in older women.
Causes and Triggers:
Several factors can contribute to breast pain:
- Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle (for cyclical mastalgia)
- Breast injuries or trauma
- Fibrocystic breast changes (benign lumps)
- Breast infections (e.g., mastitis)
- Breast cysts
- Muscle strain or sprain in the chest area
- Certain medications (e.g., hormonal contraceptives)
- Large or heavy breasts
- Stress or emotional factors
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing breast pain:
-
Age: Women in different age groups may experience different types of breast pain. Younger women are more likely to experience cyclical mastalgia due to hormonal fluctuations, while older women may develop non-cyclical mastalgia due to fibrocystic changes or other factors.
-
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause can contribute to breast pain.
-
Breastfeeding: Women who are breastfeeding may experience breast pain due to engorgement or mastitis.
-
Medications: Some hormonal medications or contraceptives can cause breast pain as a side effect.
-
Breast Size: Women with larger or heavier breasts may experience more strain on their chest muscles, leading to breast pain.
Types of Breast Pain (Mastalgia):
-
Cyclical Mastalgia: This type of breast pain is linked to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle. It typically occurs a few days before the period starts and improves after menstruation.
-
Non-Cyclical Mastalgia: Non-cyclical breast pain doesn't follow a predictable pattern related to the menstrual cycle. It can be constant or intermittent and may require further investigation to determine the underlying cause.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
-
Clinical Examination: A healthcare provider will perform a physical examination of the breasts to check for lumps, swelling, or other abnormalities.
-
Mammogram: A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast tissue. It is used to identify any lumps or changes that may require further evaluation.
-
Ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the breast tissue. It helps to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid masses.
-
Breast MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of the breast tissue and is used to further investigate any abnormalities detected in other tests.
-
Fine Needle Aspiration: If a breast lump is found, a fine needle aspiration may be performed to withdraw fluid or cells for further analysis.
-
Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be required to obtain a tissue sample for examination under a microscope to determine if the lump is benign or malignant.
Treatments:
-
Over-the-counter Pain Relievers: For mild breast pain, over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide relief.
-
Supportive Bras: Wearing a well-fitting, supportive bra can help alleviate breast pain, especially during physical activities.
-
Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the breasts can help reduce pain and swelling.
-
Hormonal Therapies: For cyclical mastalgia, hormonal therapies like birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy may be recommended to regulate hormone levels.
-
Antibiotics: If breast pain is caused by an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
-
Surgery: In rare cases where breast pain is severe and unresponsive to other treatments, surgery may be considered as a last resort.
Complications of Breast Pain (Mastalgia):
Breast pain itself is generally not harmful, but it can cause significant discomfort and anxiety. If breast pain is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as new lumps, nipple discharge, or skin changes, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to rule out potential serious conditions like breast cancer.
Prevention Techniques:
Although breast pain is not always preventable, some measures can help reduce its occurrence or severity:
-
Wear Supportive Bras: Wearing a well-fitted, supportive bra can reduce breast movement and discomfort during physical activities.
-
Limit Caffeine Intake: Some studies suggest that reducing caffeine intake may help alleviate breast pain in some individuals.
-
Manage Stress: Practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help manage hormonal fluctuations that may contribute to breast pain.
-
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can contribute to overall breast health.
breast pain (mastalgia) is a prevalent concern for many people, including women, in India. It can be categorized into cyclical and non-cyclical types, each with its unique characteristics and triggers. Timely diagnosis through clinical examinations and imaging tests is essential to determine the cause of breast pain and guide appropriate treatment. While breast pain is usually not a sign of a severe condition, it's crucial to be aware of any changes in the breasts and seek medical attention if needed. Leading a healthy
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0