Brain tumor
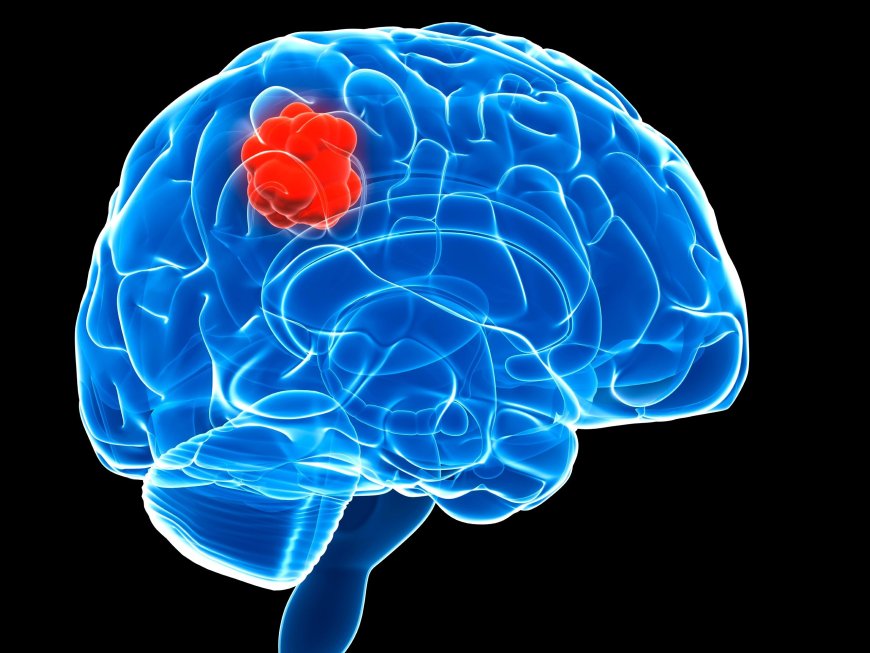
Introduction:
In India, just like in other parts of the world, people face various health challenges, and one of the significant concerns is brain tumors. Brain tumors are abnormal growths that develop in the brain and can affect a person's daily life. In this article, we will explore what brain tumors are, their signs and symptoms, classifications, causes, risk factors with examples, different types of brain tumors with detailing, diagnostic tests, treatments, and complications, along with prevention techniques.
Signs and Symptoms:
Brain tumors can manifest with various signs and symptoms, and these can vary depending on their location and size. Some common symptoms include persistent headaches, nausea, vomiting, difficulty in walking, seizures, changes in personality or behavior, and problems with vision, speech, or memory.
What Is Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor is an abnormal mass or growth that forms in the brain. The brain is a vital organ that controls our body's functions and thoughts, so when a tumor grows, it can interfere with these processes and cause health issues.
How Is Brain Tumor Classified?
Brain tumors can be classified into two main types: primary and secondary. Primary brain tumors originate in the brain itself, while secondary brain tumors (also called metastatic brain tumors) spread to the brain from other parts of the body. Primary brain tumors are further classified based on the type of cells they arise from.
Causes and Triggers:
The exact causes of brain tumors are still not fully understood, but some factors might increase the risk of developing them. These risk factors include exposure to radiation, family history of brain tumors, certain genetic conditions, and previous history of cancer. For example, if someone's family members have had brain tumors before, there might be a higher chance of them developing it as well.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Let's look at some examples of risk factors for brain tumors:
-
Radiation Exposure: If someone receives high-dose radiation treatment to the head as a part of their cancer treatment, it can increase the risk of brain tumors later in life.
-
Genetic Conditions: Some rare genetic conditions, like neurofibromatosis or Li-Fraumeni syndrome, can be associated with a higher risk of brain tumors.
-
Age: While brain tumors can affect people of all ages, certain types are more common in specific age groups. For instance, medulloblastomas are more prevalent in children.
Types of Brain Tumors:
-
Gliomas: These tumors arise from glial cells, which are supportive cells in the brain. Examples of gliomas include astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and glioblastomas.
-
Meningiomas: These tumors develop in the meninges, which are the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
-
Pituitary Adenomas: These tumors grow in the pituitary gland, a small gland in the brain responsible for hormone regulation.
-
Medulloblastomas: These are most common in children and originate in the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for coordination and balance.
-
Schwannomas: These tumors form on the nerves that connect the brain and the inner ear and can lead to hearing loss.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
Diagnosing brain tumors often requires a combination of tests:
-
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This test uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain, helping doctors locate and analyze the tumor.
-
CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain, allowing doctors to identify abnormal growths.
-
Biopsy: A small piece of the tumor is removed and examined under a microscope to determine its type and grade.
Treatments for brain tumors depend on the type, location, and size of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. Some common treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
Complications of Brain Tumors:
Brain tumors can lead to various complications, such as:
-
Neurological Deficits: Depending on the tumor's location, it can cause difficulties in speech, movement, memory, or other cognitive functions.
-
Seizures: Brain tumors can trigger seizures, which are sudden bursts of abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
-
Increased Intracranial Pressure: As the tumor grows, it can lead to increased pressure inside the skull, causing headaches and other symptoms.
Prevention Techniques:
While it's not always possible to prevent brain tumors, certain lifestyle choices may reduce the risk of developing them. These include maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation, and using helmets or protective gear during activities that could lead to head injuries.
Brain tumors are complex medical conditions that can impact a person's life in profound ways. In India and around the world, medical professionals are continually researching and developing better treatments and prevention strategies to improve the lives of those affected by brain tumors. By staying informed and taking appropriate precautions, we can contribute to a healthier future and support those who bravely battle brain tumors.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0