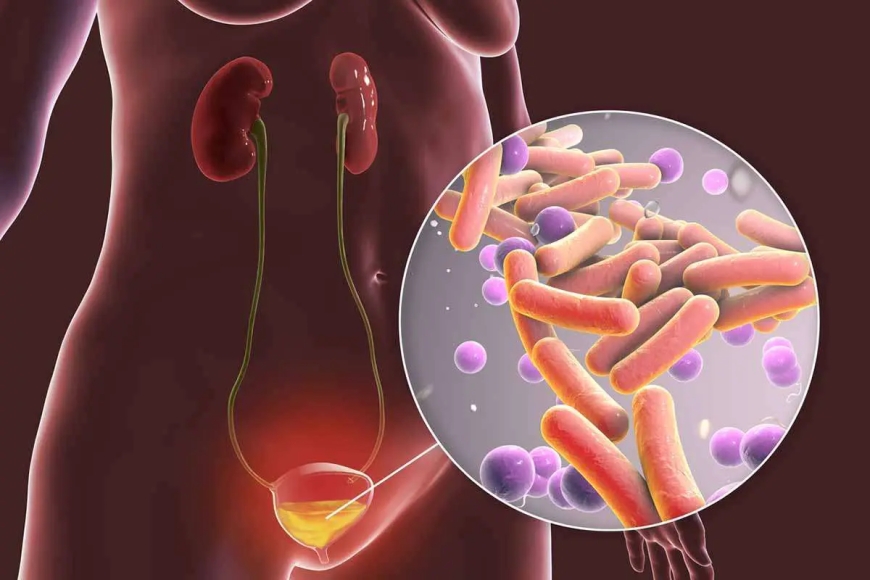
Bladder Infections in Teens and adults
Introduction:
Bladder infections, also known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), can be quite a bother for both teens and adults in India. This article aims to shed light on what bladder infections are, their symptoms, causes, classification, and the various types found in teens and adults. We will also explore the diagnostic tests used to identify them and the treatments available, along with complications and prevention techniques. So, let's embark on a journey to understand this pesky intruder that affects our urinary system.
Signs and Symptoms:
Bladder infections can cause discomfort and irritation in the urinary system. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Frequent and Urgent Urination: Feeling the need to pee more often than usual and a strong urge to go.
- Pain or Burning Sensation: Pain or a burning feeling while urinating, making it uncomfortable.
- Lower Abdominal Discomfort: Aches or cramps in the lower abdomen area.
- Cloudy or Bloody Urine: The urine might appear cloudy or have traces of blood.
- Foul-Smelling Urine: The urine might have a strong and unpleasant smell.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak due to the infection.
- Fever: In some cases, there might be a fever, indicating the infection has spread.
What Are Bladder Infections in Teens and Adults?:
Bladder infections are caused by harmful bacteria entering the urinary system, leading to inflammation and infection in the bladder. This can make it difficult for the bladder to function correctly and cause discomfort during urination.
How Are Bladder Infections Classified?:
Bladder infections are classified based on their location and severity:
- Cystitis: This is a common type of bladder infection, affecting the bladder's lining. It can cause discomfort during urination and frequent urges to pee.
- Pyelonephritis: A more severe infection that occurs when the bacteria travel up to the kidneys, leading to back pain, fever, and general weakness.
Causes and Triggers:
Bladder infections are primarily caused by harmful bacteria, most commonly E. coli, entering the urinary tract. These bacteria can come from various sources, such as improper hygiene, not drinking enough water, or using public toilets.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Several factors increase the risk of bladder infections. Examples of risk factors include:
- Female Gender: Women are more prone to bladder infections due to their shorter urethra, making it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
- Sexual Activity: Sexual activity can increase the risk of bladder infections, especially in women.
- Urinary Tract Abnormalities: Some people may have structural issues in their urinary tract, making infections more likely.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can promote bacterial growth and increase the risk of infections.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV or certain medications can weaken the immune system, making infections more likely.
Types of Bladder Infections in Teens and Adults:
- Cystitis: As mentioned earlier, this type of infection affects the bladder's lining and causes frequent urination, pain, and discomfort.
- Pyelonephritis: A more severe infection that affects the kidneys. It can cause back pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
To diagnose and treat bladder infections, doctors may use the following tests and treatments:
- Urinalysis: This involves analyzing a urine sample to check for signs of infection, such as the presence of bacteria or white blood cells.
- Urine Culture: A sample of urine is collected and cultured to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. This helps choose the right antibiotic for treatment.
- Antibiotics: Once the bacteria causing the infection are identified, doctors prescribe specific antibiotics to fight the infection.
- Drinking Plenty of Fluids: It's essential to drink lots of water to flush out the bacteria and promote healing.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help reduce discomfort during urination.
Complications of Bladder Infections in Teens and Adults:
If left untreated, bladder infections can lead to severe complications, such as kidney infections, sepsis (a life-threatening condition), and recurrent infections.
Prevention Techniques:
To prevent bladder infections, you can follow these simple tips:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water every day.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Always wipe from front to back after using the toilet and wash hands regularly.
- Urinate When Needed: Don't hold in your pee; go when you feel the urge.
- Avoid Irritants: Stay away from foods and drinks that can irritate your bladder, like spicy foods, caffeine, and soda.
- Wear Cotton Underwear: Cotton allows better airflow, reducing the risk of infection.
if you ever experience symptoms like pain while peeing or feeling like you have to go all the time, talk to your parents or a doctor. They can help you get the right treatment and keep your bladder healthy!
What's Your Reaction?