Bladder Infections in Children
Introduction:
Bladder infections, also known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), are common among children in India and around the world. A bladder infection occurs when harmful bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, leading to discomfort and sometimes serious complications. In this article, we will learn about the signs and symptoms, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention techniques for bladder infections in children.
Signs and Symptoms:
When a child has a bladder infection, they may experience the following symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating
- Strong-smelling urine
- Cloudy or pinkish urine (blood in the urine)
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Fever
- Vomiting or nausea
What Is Bladder Infections in Children?
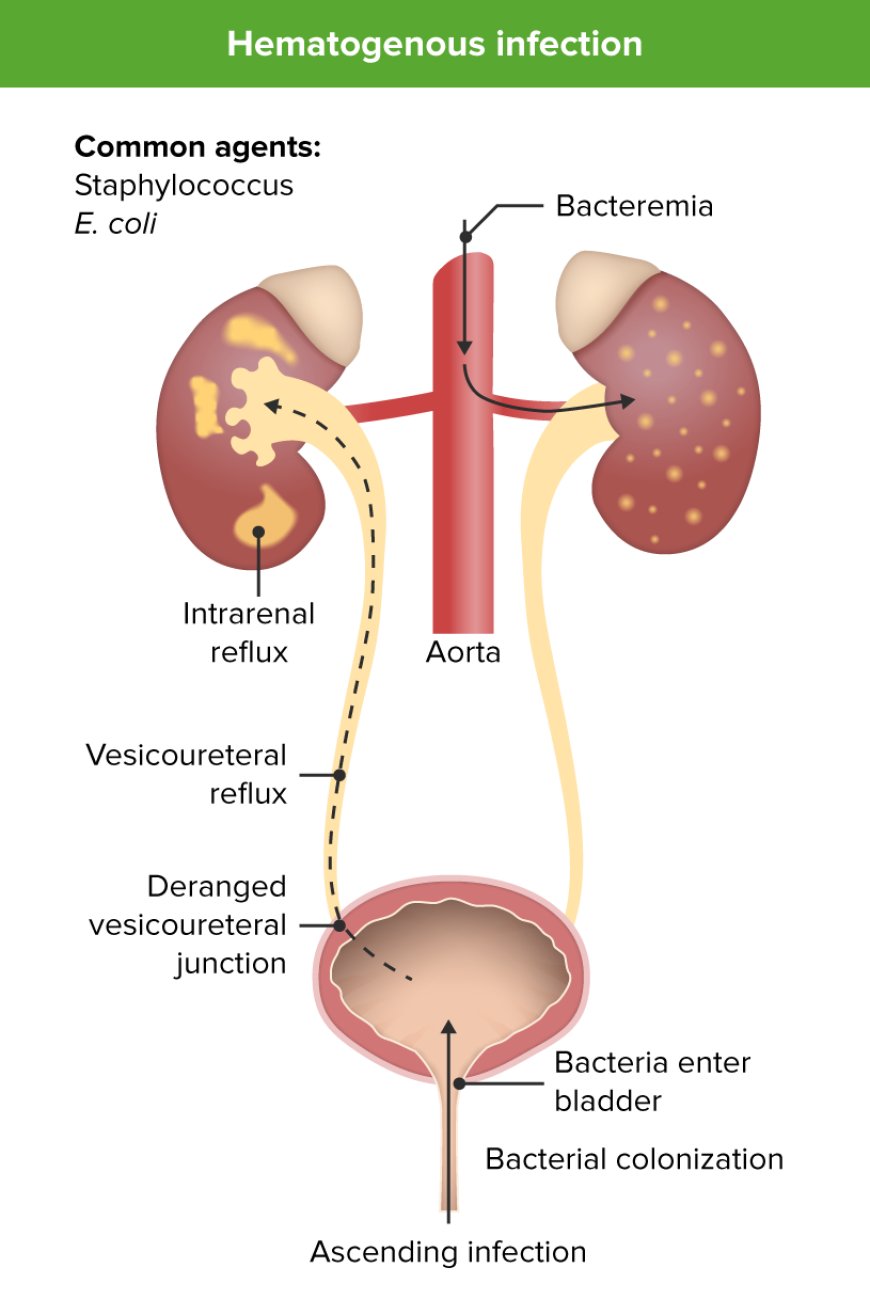
A bladder infection is a type of bacterial infection that affects the urinary tract, including the bladder. The urinary tract is the pathway that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder and out of the body.
How Is Bladder Infections in Children Classified?
Bladder infections in children can be classified based on the location of the infection:
- Lower UTI: When the infection is limited to the bladder.
- Upper UTI: When the infection involves the kidneys as well.
Causes and Triggers:
Bladder infections are usually caused by bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally live in the intestines. These bacteria can enter the urinary tract through the urethra (the tube through which urine leaves the body) and multiply in the bladder. Some common triggers that can increase the risk of bladder infections in children include:
- Holding urine for too long, which can allow bacteria to grow in the bladder.
- Not wiping properly after using the bathroom, allowing bacteria to enter the urethra.
- Tight clothing that can trap moisture and create a favorable environment for bacterial growth.
- Poor hygiene practices.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Certain factors can increase the risk of bladder infections in children. Let's understand these risk factors with examples:
- Gender: Girls are more prone to bladder infections because their urethra is shorter, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
- Uncircumcised Boys: Uncircumcised boys have a higher risk as bacteria can accumulate under the foreskin.
- Structural Abnormalities: Some children may be born with structural issues in the urinary tract, making infections more likely.
- Constipation: Infrequent bowel movements can put pressure on the bladder and increase the risk of infection.
Types of Bladder Infections in Children:
- Acute Uncomplicated UTI: This type affects an otherwise healthy child with a normal urinary tract. It is common and usually resolves with proper treatment.
- Recurrent UTI: When a child experiences multiple UTIs over a short period, it's called recurrent UTI. It may indicate an underlying issue.
- Febrile UTI: Infections accompanied by a high fever are called febrile UTIs and require prompt medical attention.
- Asymptomatic Bacteriuria: Sometimes, bacteria may be present in the urine without causing symptoms. It is important to identify and treat this to prevent complications.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
-
Urinalysis: This is a simple urine test that helps detect the presence of bacteria, blood cells, and other substances that may indicate an infection. Treatment: Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat bladder infections. Make sure to complete the entire course as prescribed by the doctor.
-
Urine Culture: This test identifies the specific bacteria causing the infection and helps determine the most effective antibiotic for treatment. Treatment: Antibiotics are used based on the results of the urine culture.
Complications of Bladder Infections in Children:
If left untreated, bladder infections can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney infections, which may cause kidney damage. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to avoid these complications.
Prevention Techniques:
To prevent bladder infections in children, follow these simple steps:
- Encourage proper hygiene practices, including regular handwashing and proper wiping after using the bathroom.
- Make sure your child drinks plenty of water throughout the day to flush out bacteria.
- Avoid tight clothing that can trap moisture and promote bacterial growth.
- Teach your child to use the bathroom regularly and avoid holding urine for too long.
Bladder infections in children can be uncomfortable and sometimes serious if not treated promptly. By recognizing the signs and symptoms and following preventive measures, parents can help their children stay healthy and avoid bladder infections. Remember, if your child experiences any symptoms of a bladder infection, seek medical attention to ensure a timely and appropriate treatment. Stay healthy, stay happy!
What's Your Reaction?