Bladder cancer
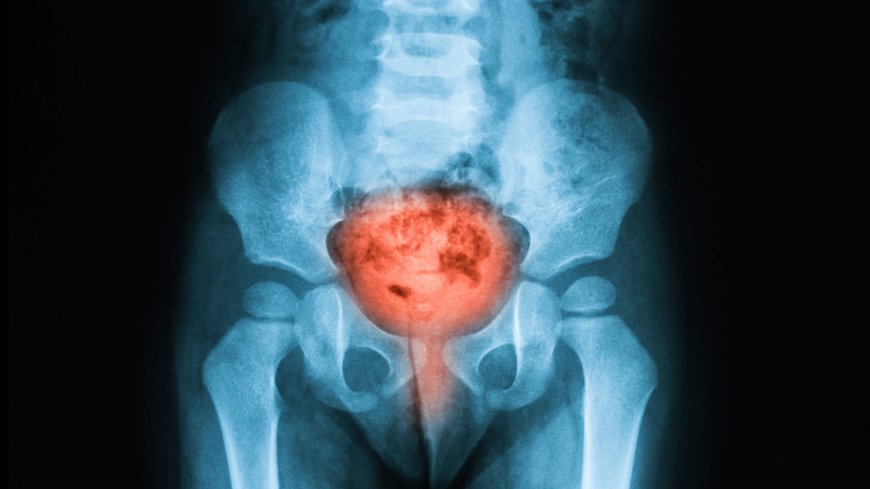
Introduction:
Bladder cancer is a disease that affects the bladder, a small organ in the lower part of the abdomen. The bladder is responsible for storing urine before it is released from our bodies. While bladder cancer can affect people of all ages, it is more common in older adults. Let's explore what bladder cancer is, its signs and symptoms, types, causes, risk factors, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention techniques in simple language that even 10-year-old children can easily understand.
Signs and Symptoms:
Bladder cancer can show various signs and symptoms, which might include:
-
Blood in Urine: One of the most common signs is seeing blood in the urine. The urine may look pink, red, or sometimes like cola due to the presence of blood.
-
Frequent Urination: Feeling the need to urinate more often than usual, even when the bladder is not full.
-
Pain or Burning Sensation: Feeling pain or a burning sensation while passing urine.
-
Back or Pelvic Pain: Experiencing pain in the lower back or pelvic area.
-
Changes in Urination: Having difficulty urinating, weak urine stream, or feeling like the bladder is not empty even after urination.
What Is Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the bladder. These abnormal cells form a tumor, which can be cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign). Malignant tumors are dangerous as they can spread to other parts of the body.
How Is Bladder Cancer Classified?
Bladder cancer can be classified into two main types:
-
Non-Invasive Bladder Cancer: In this type, cancer cells are only present in the inner lining of the bladder and have not spread to deeper layers or other organs.
-
Invasive Bladder Cancer: In this type, cancer cells have spread to deeper layers of the bladder or even to nearby organs and tissues.
Causes and Triggers:
The exact cause of bladder cancer is not always clear, but certain factors can increase the risk of developing the disease. Some of these risk factors include:
-
Smoking: Smoking tobacco is one of the most significant risk factors for bladder cancer. It releases harmful chemicals into the body that can damage the bladder lining.
-
Exposure to Harmful Chemicals: Being exposed to certain chemicals in workplaces like dye, rubber, and chemical industries may increase the risk.
-
Chronic Bladder Infections: Frequent or long-lasting bladder infections can also increase the risk.
-
Age: The risk of bladder cancer increases with age, especially in people over 55.
-
Gender: Men are more likely to develop bladder cancer than women.
Types of Bladder Cancer:
Bladder cancer can be further classified based on the type of cells involved. The main types are:
-
Transitional Cell Carcinoma: This is the most common type, which starts in the cells lining the bladder.
-
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This type starts in thin, flat cells and is linked to chronic bladder infections or irritation.
-
Adenocarcinoma: This type starts in mucus-producing cells in the bladder.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
If a person shows symptoms of bladder cancer or falls under the risk categories, doctors may perform several diagnostic tests:
-
Urinalysis: This simple test checks the urine for blood, abnormal cells, or signs of infection.
-
Cystoscopy: During a cystoscopy, a tiny camera is inserted into the bladder to check for abnormal growths or tumors.
-
Biopsy: If suspicious growths are found, a small piece of tissue is taken for examination.
-
Imaging Tests: Tests like CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound help determine the extent of cancer spread.
Treatments for bladder cancer depend on the type and stage of cancer. They may include surgery to remove the tumor, chemotherapy to kill cancer cells, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy to boost the body's immune system to fight cancer cells.
Complications of Bladder Cancer:
Bladder cancer, if not treated early, can lead to serious complications. It can spread to nearby organs like the liver, lungs, or bones, making treatment difficult.
Prevention Techniques:
While some risk factors like age and gender cannot be changed, there are things we can do to reduce the risk of bladder cancer:
-
Avoid smoking and exposure to harmful chemicals.
-
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water daily.
-
Maintain a healthy diet with fruits and vegetables.
-
Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy body weight.
-
Seek prompt treatment for chronic bladder infections.
Bladder cancer is a serious condition that requires attention and care. Knowing the signs, staying away from harmful chemicals, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of bladder cancer. Regular check-ups with doctors can ensure early detection and successful treatment, allowing people to lead healthy lives in India and around the world.
What's Your Reaction?